Contents
Introduction to Cable bus vs bus duct
In the realm of electrical distribution systems, cable bus and bus duct are two prevalent methods used to transmit power within industrial, commercial, and even residential settings. While both serve the fundamental purpose of carrying electrical currents, they exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of design, application, and performance. Understanding the nuances between cable bus and bus duct is essential for selecting the most suitable solution for specific electrical infrastructure requirements.

What is Cable Bus?
Cable bus is a robust and flexible electrical power distribution system designed to accommodate high voltage and current levels. It consists of insulated conductors housed within a protective enclosure, typically constructed from galvanized steel or aluminum. The conductors, usually made of copper or aluminum, are arranged in parallel configuration, providing a reliable pathway for electricity transmission.
Advantages of Cable Bus
1. Enhanced Flexibility:
Cable bus systems offer greater flexibility in terms of installation, allowing for custom configurations to suit varying project specifications. This versatility makes cable bus particularly well-suited for applications requiring intricate routing or those with spatial constraints.
2. High Fault Tolerance:
Due to its durable construction and robust design, cable bus exhibits excellent resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stresses. This inherent resilience enhances the system’s reliability and reduces the likelihood of power interruptions due to faults.
3. Scalability:

Cable bus systems can be easily expanded or modified to accommodate future growth or changes in electrical demand. This scalability feature ensures that the infrastructure remains adaptable to evolving operational requirements, thereby optimizing long-term investment value.
Discuss the advantages of cable bus over bus duct.
- Durability: Cable bus systems are highly resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and corrosive substances, making them ideal for outdoor use.
- Reliability: With fewer joints and connections compared to bus duct, cable bus offers enhanced reliability and lower risk of electrical faults or failures.
- Installation: Cable bus installation is typically faster and requires fewer components than bus duct, resulting in reduced labor costs and construction time.
What is bus duct?
An Overview of Bus Duct
Bus duct is a compact and efficient means of electrical power distribution, typically employed in medium to low voltage applications. It comprises a metal enclosure housing multiple conductors, usually made of copper or aluminum, arranged in a predefined configuration.
Key Features and Benefits
1. Space Optimization:
Bus duct systems are renowned for their space-saving design, making them ideal for installations where real estate is limited. By eliminating the need for traditional cable runs, bus ducts help streamline the layout of electrical infrastructure, thereby maximizing available space for other purposes.
2. Simplified Maintenance:
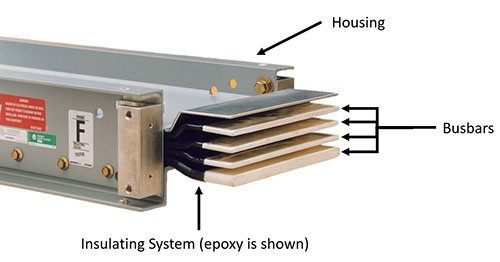
The modular construction of bus duct facilitates easier maintenance and servicing operations compared to conventional wiring systems. This accessibility ensures quicker fault identification and resolution, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
3. Cost-Effectiveness:
While the initial investment in bus duct systems may be higher than traditional wiring methods, the long-term cost benefits are significant. Reduced installation time, lower material requirements, and simplified maintenance contribute to overall cost savings throughout the lifecycle of the infrastructure.
Comparison of Cable Bus and Bus Duct
When deciding between cable bus and bus duct, it’s essential to consider various factors such as design, materials, flexibility, and cost.
- Design: Cable bus consists of individual conductors bundled together, while bus duct contains conductors housed within a single enclosure.
- Materials: Cable bus conductors are typically made of copper or aluminum, enclosed in a steel or aluminum casing. Bus duct conductors may also use copper or aluminum, enclosed in a steel or aluminum housing.
- Applications: Cable bus is often used for outdoor applications or in harsh environments where protection from weather and contaminants is necessary. Bus duct is commonly employed for indoor installations, offering flexibility in routing and space-saving advantages.
- Cost Comparison: Cable bus may have higher initial costs due to materials and installation expenses but can offer long-term savings through reduced maintenance and enhanced reliability. Bus duct may be more cost-effective for smaller installations or projects where flexibility and space utilization are primary concerns.
Conclusion
In summary, both cable bus and bus duct represent viable solutions for electrical power distribution, each offering distinct advantages based on specific requirements and operational considerations. While cable bus excels in flexibility and fault tolerance, bus duct stands out for its space optimization and cost-effectiveness. Both cable bus and bus duct have their strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications and environments. By understanding the key differences and considering factors such as durability, flexibility, and cost, you can make an informed decision when choosing between cable bus and bus duct for your electrical distribution needs.

