Contents
- 1 Cable Fire Safety and Prevention Tips
- 2 The Fire Triangle
- 3 15 Known Sources of Electrical Fires
- 4 Electrical Fire Safety Tips
- 5 Conclusion
- 6 FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- 7 1. How often should electrical cables be inspected for safety?
- 8 2. What are common signs of cable damage that indicate a potential fire hazard?
- 9 3. Are there specific safety standards for electrical cables and components?
- 10 4. How can I protect cables from damage in high-traffic areas?
- 11 5. What should I do if I encounter a cable fire?
Cable Fire Safety and Prevention Tips
In both residential and commercial settings, electrical fires caused by faulty cables pose a significant risk to life and property. Understanding cable fire safety and implementing preventive measures are essential steps in maintaining a safe environment. This article provides comprehensive guidance on cable fire safety and prevention tips to minimize the risk of fire incidents.

The Fire Triangle
The fire triangle is a fundamental concept that illustrates the three elements required for a fire to ignite and sustain itself: heat, fuel, and oxygen. Understanding these components is crucial for fire prevention and suppression.
- Heat: Heat is the initial energy source that raises the temperature of a material to its ignition point. Heat sources can include open flames, electrical sparks, friction, or radiant heat from nearby sources.
- Fuel: Fuel refers to any combustible material capable of sustaining a fire. Common fuels include wood, paper, cloth, plastics, gases, and liquids. The type and amount of fuel present determine the intensity and duration of the fire.
- Oxygen: Oxygen is the oxidizing agent that enables combustion to occur. It combines with the fuel in the presence of heat, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. Sufficient oxygen levels are essential for sustaining a fire.
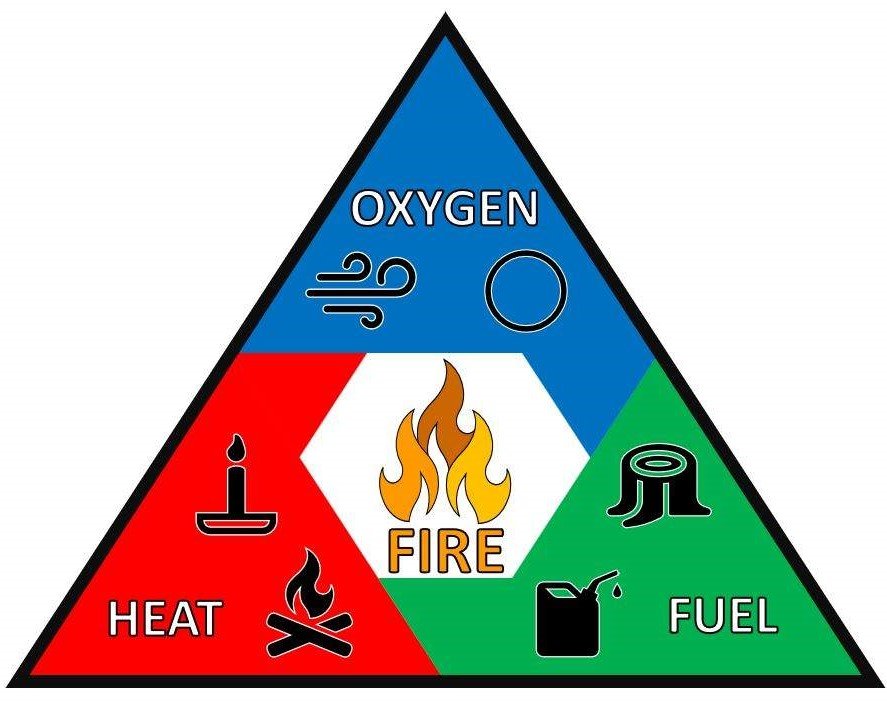
When all three elements—heat, fuel, and oxygen—are present in the right proportions, a fire can ignite and continue to burn. Removing any one of these elements can extinguish the fire or prevent it from starting in the first place. This principle forms the basis of fire safety practices, including fire prevention measures, firefighting techniques, and the design of fire suppression systems.
15 Known Sources of Electrical Fires
- Faulty Wiring: Poorly installed or damaged wiring can lead to electrical fires due to short circuits or overloading.
- Electrical Appliances: Malfunctioning appliances with damaged cords or faulty components pose a significant fire risk.
- Overloaded Circuits: Overloading circuits with too many devices or appliances can cause overheating and electrical fires.
- Extension Cords: Improper use or overloading of extension cords can result in overheating and ignition of nearby combustible materials.
- Light Fixtures: Faulty wiring, loose connections, or improper installation of light fixtures can lead to electrical fires.
- Power Strips: Overloading power strips by plugging in too many devices can cause overheating and fire hazards.
- Electrical Outlets: Damaged or outdated electrical outlets can spark fires, especially if exposed to moisture or debris.
- Space Heaters: Misuse or placement of space heaters near flammable materials can lead to ignition and electrical fires.
- Faulty Circuit Breakers: Aging or defective circuit breakers may fail to trip in case of overload, leading to overheating and fires.
- Kitchen Appliances: Improper maintenance or misuse of kitchen appliances like toasters, microwaves, and ovens can cause electrical fires.
- Old Wiring Systems: Outdated wiring systems, such as knob-and-tube or aluminum wiring, pose a higher risk of electrical fires.
- Electrical Panels: Overloaded or poorly maintained electrical panels can cause sparks and fires due to overheating.
- Lightning Strikes: Lightning strikes can cause power surges and electrical fires, especially in buildings without proper surge protection.
- HVAC Systems: Faulty wiring or components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems can lead to electrical fires.
- DIY Electrical Work: Improper or amateur electrical work done by unqualified individuals can result in wiring faults and fire hazards.

Electrical Fire Safety Tips
- Inspect Regularly: Conduct routine inspections of electrical outlets, wiring, and appliances to check for signs of damage or wear.
- Professional Installation: Hire qualified electricians for electrical installations, repairs, and upgrades to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not overload electrical outlets or power strips with too many devices or appliances to prevent overheating.
- Use Surge Protectors: Install surge protectors to safeguard electronic devices from power surges caused by lightning or electrical faults.
- Replace Damaged Cords: Replace frayed or damaged electrical cords immediately to prevent electrical sparks and fires.
- Keep Flammables Away: Keep flammable materials like curtains, rugs, and furniture away from heat sources and electrical appliances.
- Unplug Unused Devices: Unplug devices and appliances when not in use to reduce the risk of electrical fires caused by faulty connections.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation around electrical equipment to prevent overheating and fire hazards.
- Space Heater Safety: Use space heaters with caution, keeping them away from combustible materials and never leaving them unattended.
- Smoke Alarms: Install smoke alarms on every level of your home and test them regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Fire Extinguishers: Keep fire extinguishers accessible and ensure everyone in the household knows how to use them in case of emergencies.
- Educate Family Members: Teach family members about electrical safety practices, including how to respond to electrical fires and when to evacuate.
- Emergency Plan: Develop and practice an emergency evacuation plan with your family, including a designated meeting point outside the home.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about electrical safety guidelines and best practices to reduce the risk of electrical fires in your home.
- Report Concerns Promptly: If you notice any electrical issues or concerns, such as flickering lights or sparking outlets, address them promptly by contacting a licensed electrician.
Conclusion
Cable fire safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and secure environment in homes, workplaces, and public spaces. By implementing preventive measures such as regular inspection, proper installation, and use of high-quality materials, the risk of cable-related fire incidents can be significantly reduced. Additionally, promoting fire safety awareness and providing adequate training to personnel are essential steps in mitigating fire risks and ensuring the safety of occupants.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How often should electrical cables be inspected for safety?
2. What are common signs of cable damage that indicate a potential fire hazard?
3. Are there specific safety standards for electrical cables and components?
4. How can I protect cables from damage in high-traffic areas?
5. What should I do if I encounter a cable fire?

