Contents
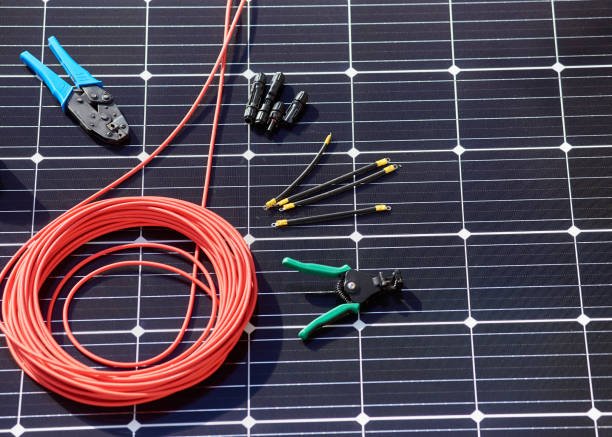
Introduction to Cable for Solar Panels
When embarking on the journey of setting up a solar energy system, one of the fundamental elements to consider is the choice of cables. These seemingly simple components play a crucial role in the efficiency and performance of your solar panels. Essentially, solar panel cables serve as the vital link between the panels themselves and your home or the grid, facilitating the transfer of generated energy.

In this introductory segment, we’ll delve into the significance of selecting the right cables for your solar setup. We’ll explore how the proper wiring not only ensures smooth energy transfer but also contributes to the overall effectiveness and longevity of your solar panel system. So, let’s illuminate the path to understanding solar panel cables and their pivotal role in harnessing the power of the sun.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Solar Panel Cables
When it comes to selecting the appropriate cables for your solar panel system, several crucial factors demand consideration. Each aspect plays a pivotal role in determining the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your solar energy setup. Let’s explore these factors in detail:
- Gauge: The gauge of the cable is paramount as it directly influences the amount of current it can carry without experiencing excessive voltage drop. Choosing the right gauge ensures that your solar panels can deliver their maximum output efficiently.
- Material: Copper is the most commonly used material for solar panel cables due to its excellent conductivity. However, consider alternatives such as aluminum or tinned copper for enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in environments prone to moisture or salt exposure.
- Weather Resistance: Solar panel cables are often exposed to harsh outdoor conditions, including sunlight, rain, and temperature fluctuations. Opt for cables with robust insulation and UV-resistant jackets to withstand these elements and maintain performance over time.
- Length: The distance between your solar panels and the inverter determines the length of cable needed. Longer cable runs require thicker gauges to mitigate voltage drop and ensure efficient energy transmission.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the cables you choose are compatible with your solar panels, inverters, and other components of your solar energy system. Compatibility issues can lead to inefficiencies and potential safety hazards.
By carefully considering these factors and making informed decisions, you can ensure that your solar panel cables are tailored to meet the specific requirements of your installation. This proactive approach not only optimizes the performance of your solar energy system but also enhances its reliability and safety for years to come.
AC and DC Solar Panels
When it comes to solar panel systems, there are two primary types of electricity used: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Understanding the differences between AC and DC solar panels is essential for designing and operating an efficient solar energy system.
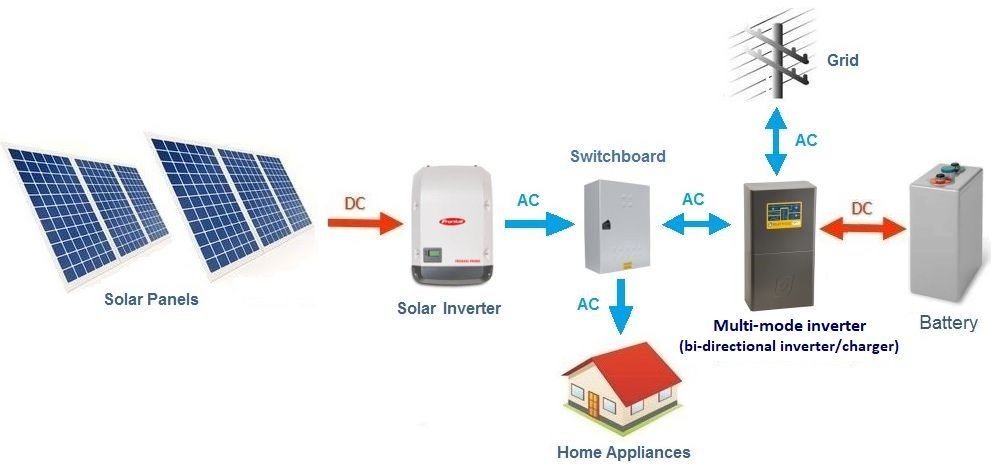
DC Solar Panels:
DC solar panels generate electricity in the form of direct current (DC), which is the same type of electricity produced by batteries. Photovoltaic (PV) cells within the solar panels convert sunlight directly into DC electricity. DC electricity flows continuously in one direction, making it well-suited for powering devices that operate on DC, such as lights, appliances, and electronics. In off-grid solar systems or those with battery storage, DC electricity is often used to charge batteries for later use or to power DC appliances directly.
AC Solar Panels:
AC solar panels generate electricity in the form of alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses. In AC solar panels, an inverter converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity suitable for use in the electrical grid or for powering household appliances. AC electricity periodically reverses direction, making it more suitable for long-distance transmission and for powering most household appliances and devices.
Choosing between AC and DC solar panels depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your solar energy system, whether you’re connecting to the grid, and whether you have battery storage.
- Off-Grid Systems: Off-grid systems typically use DC solar panels paired with batteries to store electricity for use when the sun isn’t shining.
- Grid-Tied Systems: Grid-tied systems often use AC solar panels, as they allow for seamless integration with the electrical grid. Excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be fed back into the grid for credit or compensation.
Ultimately, the decision between AC and DC solar panels depends on your specific needs, preferences, and the requirements of your solar energy system. Consulting with a qualified solar installer can help you determine the best option for your particular circumstances.
Types of Solar Panel Cables
When it comes to wiring solar panels, selecting the right cable types is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety of your solar energy system. Here are the main types of cables used for connecting solar panels:
PV Wire:
PV (Photovoltaic) wire is specifically designed for solar applications. It is built to withstand outdoor conditions, including exposure to sunlight and extreme temperatures. PV wire is insulated and often UV-resistant, making it suitable for use in both rooftop and ground-mounted solar installations.
USE-2 Cable:
Underground Service Entrance (USE-2) cable is commonly used for wiring solar panels in outdoor or buried applications. It is designed to withstand exposure to moisture and direct burial in the ground. USE-2 cable is typically used for longer cable runs between solar panels and other system components such as inverters and charge controllers.
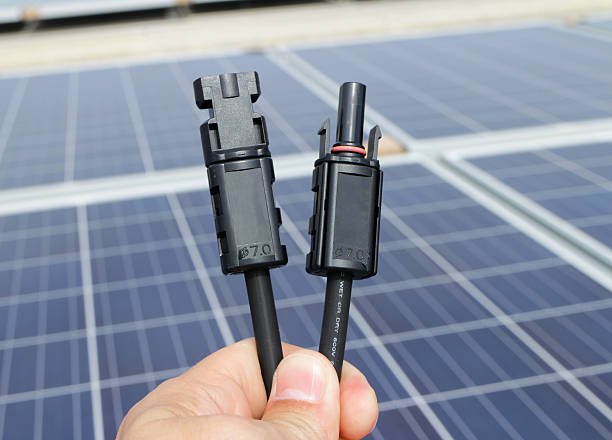
MC4 Cables:
MC4 cables are equipped with MC4 connectors on each end, making them easy to connect and disconnect without the need for special tools. These connectors are widely used in solar panel installations for their reliability and ease of installation. MC4 cables are typically used to connect solar panels in series or parallel configurations.
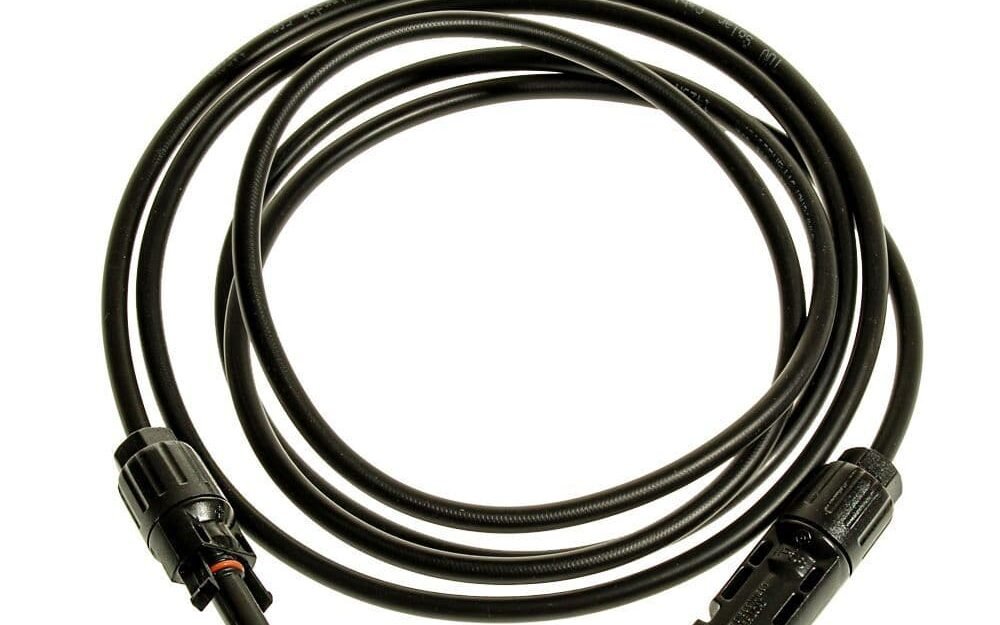

When choosing cable types for your solar panel installation, consider factors such as the length of cable runs, voltage and current ratings, weather resistance, and compatibility with your solar panels and other system components. Using high-quality cables that are properly sized and rated for your installation will help ensure the efficiency, reliability, and safety of your solar energy system.
Selecting the Right Cable Gauge
Choosing the appropriate cable gauge is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of your solar panel system. The gauge of a cable refers to its thickness or diameter, which directly affects its ability to carry electrical current without experiencing excessive voltage drop. Here’s a brief guide to selecting the right cable gauge for your solar panel installation:
- Determine Maximum Current: Start by determining the maximum current that will flow through the cables in your solar panel system. This can be calculated based on the total wattage of your solar panels and the system’s voltage.
- Consider Cable Length: Next, consider the length of the cable runs between your solar panels and the inverter or other system components. Longer cable runs result in greater resistance and voltage drop, requiring thicker gauge cables to compensate.
- Consult Voltage Drop Charts: Use voltage drop charts or online calculators to determine the appropriate cable gauge for your specific installation. These tools take into account factors such as cable length, current flow, and acceptable voltage drop to recommend the optimal gauge.
- Err on the Side of Caution: It’s generally advisable to choose a slightly thicker gauge than strictly necessary to minimize voltage drop and ensure reliable performance, especially for longer cable runs.
- Consider Future Expansion: If you anticipate expanding your solar panel system in the future, it’s wise to install cables with a larger gauge than currently required to accommodate potential increases in current flow.
By carefully selecting the right cable gauge based on the maximum current, cable length, and voltage drop considerations, you can ensure that your solar panel system operates efficiently and effectively, maximizing energy production and minimizing potential issues due to voltage drop.
Budget Considerations
When planning your solar panel setup, it’s crucial to balance quality with cost-effectiveness, especially when it comes to selecting cables. Here’s how to make budget-savvy decisions without compromising on performance:
Prioritize Durability:
While it may be tempting to opt for the cheapest cables available, investing in durable cables can save you money in the long run. Look for cables with robust insulation and weather-resistant jackets that can withstand the rigors of outdoor use. Though they may come with a slightly higher upfront cost, durable cables require less maintenance and are less likely to degrade over time, ultimately saving you money on repairs and replacements.
Factor in Long-Term Savings:
Consider the potential long-term savings associated with high-quality cables. By investing in cables that are built to last, you can reduce the need for frequent replacements and repairs, saving both time and money in the future. Additionally, efficient cables can help maximize the performance of your solar panel system, leading to greater energy production and lower electricity bills over time.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, selecting the right cables for your solar panel system is essential for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and longevity. By carefully considering factors such as cable gauge, material, and weather resistance, you can make informed decisions that align with your budget constraints while still meeting your specific needs. Investing in high-quality cables may require a slightly higher upfront cost, but the long-term savings in reduced maintenance and improved efficiency make it a worthwhile investment for any solar energy system.

