Contents
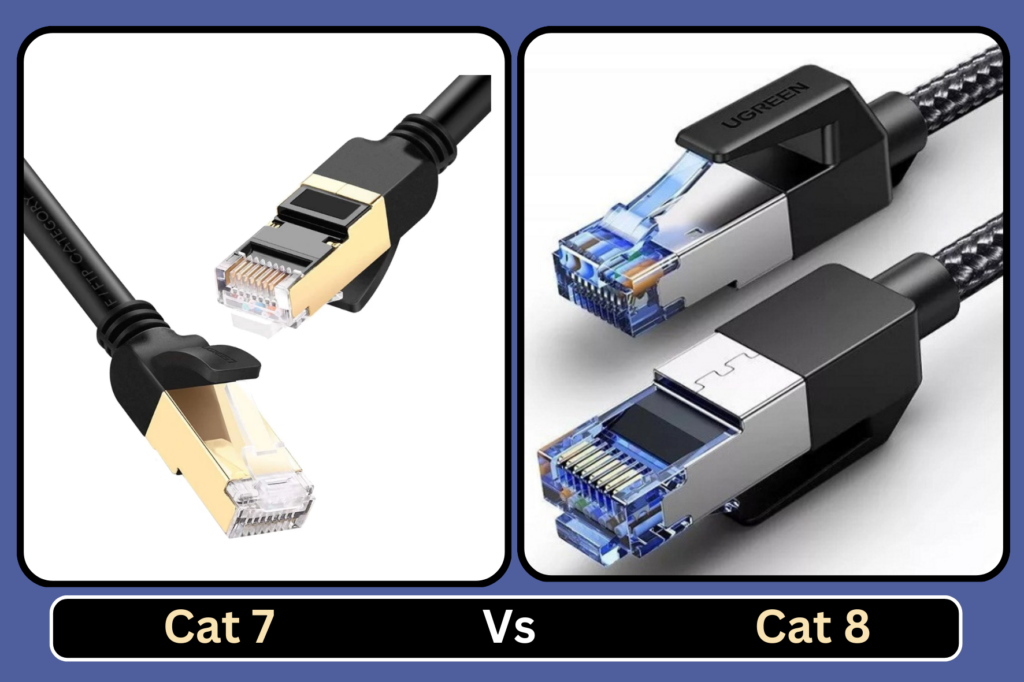
Cat 7 vs Cat 8 Ethernet Cables
In the realm of networking, the choice of Ethernet cables plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal connectivity and performance. As technology advances, newer iterations such as Cat 7 and Cat 8 have emerged, each promising enhanced features and capabilities. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the difference between cat 7 and cat 8 Ethernet cables, shedding light on their disparities and aiding you in making an informed decision for your networking needs.
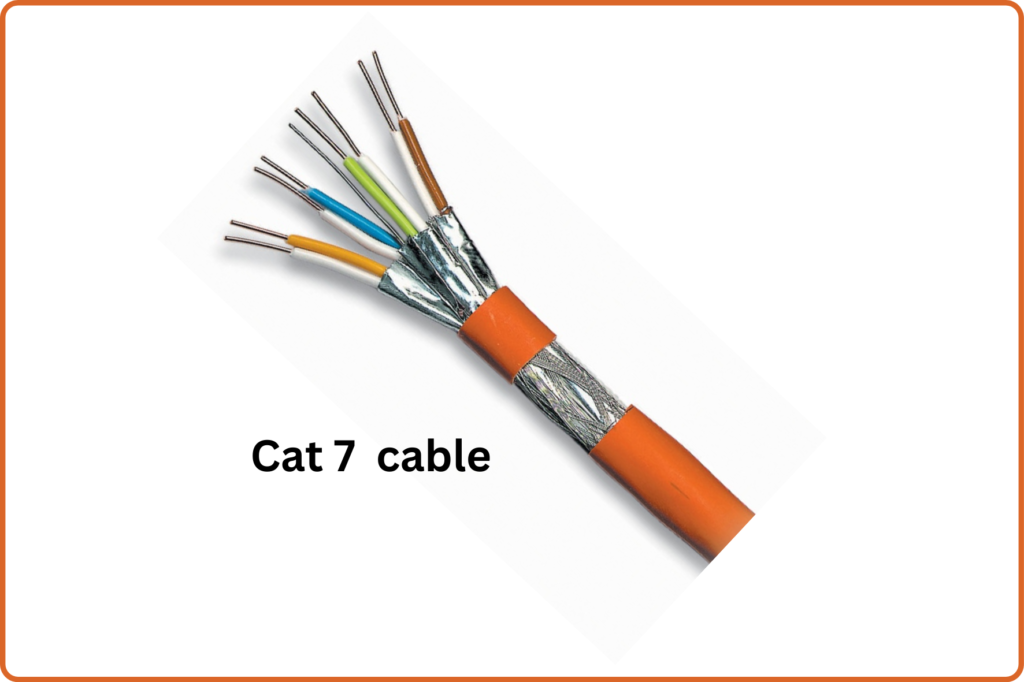
Cat 7 Ethernet Cables
Cat 7, short for Category 7, represents a high-speed Ethernet cable designed to support bandwidths of up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) over a distance of 100 meters. Characterized by its robust shielding and twisted pair design, Cat 7 cables excel in minimizing interference and crosstalk, thus ensuring reliable data transmission even in environments prone to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Features of Cat 7 Ethernet Cables
-
- Enhanced Shielding: Cat 7 cables typically feature multiple layers of shielding, including individual shielding for each pair of wires as well as an overall shield, offering superior protection against external interference.
- Twisted Pair Design: The twisted pair configuration of Cat 7 cables helps mitigate signal degradation and ensures consistent performance, especially over extended distances.
- Backward Compatibility: Despite its advanced specifications, Cat 7 cables remain compatible with lower category cables such as Cat 6 and Cat 5e, facilitating seamless integration into existing network infrastructures.
Pros & Cons of Cat 7 Cable
Pros of Cat 7 Cables:
-
- High Performance: Cat 7 cables offer impressive data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps, making them suitable for demanding networking applications.
- Effective Shielding: With shielding options like individually shielded pairs (S/FTP) or overall shielding (F/FTP), Cat 7 cables minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) for stable performance.
- Backward Compatibility: Cat 7 cables are backward compatible with lower category cables, ensuring compatibility with existing network infrastructure.
Cons of Cat 7 Cables:
-
- Limited Speed and Bandwidth: While Cat 7 cables provide high-speed performance, they fall short in comparison to the speeds achievable with Cat 8 cables.
- Cost: Cat 7 cables can be more expensive compared to lower category cables, making them less cost-effective for some installations.
- Installation Complexity: Due to their thicker gauge and shielding, Cat 7 cables may be more challenging to install than lower category cables.
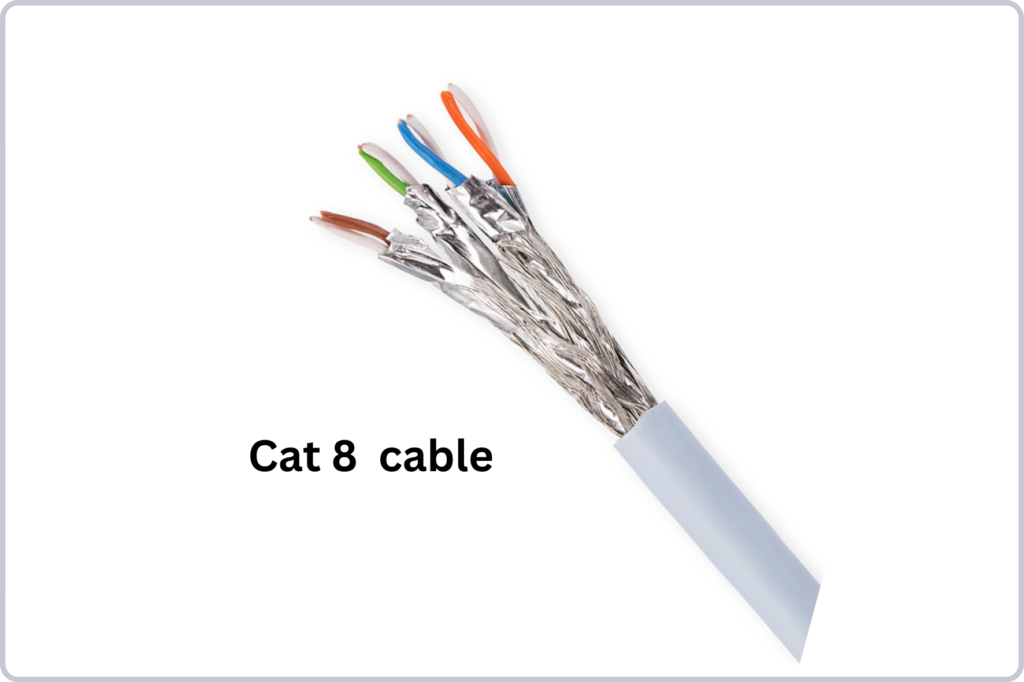
Cat 8 Ethernet Cables
In the pursuit of faster and more reliable networking solutions, Cat 8 Ethernet cables emerge as the next evolution in Ethernet cable technology. Designed to support bandwidths of up to 40 Gbps over shorter distances, Cat 8 cables represent a significant leap forward in terms of speed and performance.
Key Attributes of Cat 8 Ethernet Cables
-
- Higher Bandwidth: With its ability to deliver speeds of up to 40 Gbps, Cat 8 cables are well-suited for bandwidth-intensive applications such as high-definition video streaming and large file transfers.
- Improved Shielding: Building upon the foundation laid by Cat 7 cables, Cat 8 cables feature enhanced shielding techniques to minimize interference and ensure stable connectivity in demanding environments.
- Limited Distance: It’s important to note that while Cat 8 cables offer impressive speeds, their optimal performance is limited to shorter distances, typically up to 30 meters.
Pros & Cons of Cat 8 Cable
Pros of Cat 8 Cables:
-
- Ultra-High Speeds: Cat 8 cables support data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps, making them ideal for high-speed networking applications.
- Enhanced Shielding: Cat 8 cables feature advanced shielding, such as fully shielded twisted pairs (S/FTP), providing superior protection against crosstalk and interference.
- Future-Proofing: Investing in Cat 8 cables offers future-proofing benefits, ensuring compatibility with upcoming technologies and higher network speeds.
Cons of Cat 8 Cables:
-
- Higher Cost: Cat 8 cables are typically more expensive than lower category cables, making them a significant investment for some installations.
- Limited Distance: Cat 8 cables have a shorter maximum transmission distance compared to lower category cables, with optimal performance up to 30 meters.
- Specialized Equipment: To fully leverage the capabilities of Cat 8 cables, compatible networking equipment is required, adding to the overall cost of deployment.
Difference between Cat5e and Cat6 Ethernet Cable
difference between Cat 7 and Cat 8 (Comparison)
When comparing Cat 7 and Cat 8 Ethernet cables, several factors come into play, influencing the suitability of each for specific applications.
Construction and Specifications
-
- Cat 7 cables, also known as Category 7 cables, are designed to support frequencies of up to 600 MHz. They typically feature twisted pairs of copper wires, often with shielding to minimize interference. Cat 7 cables adhere to the TIA/EIA-568-B and ISO/IEC 11801 standards.
- Cat 8 cables represent the latest advancement in Ethernet cable technology. These cables are capable of supporting frequencies of up to 2000 MHz, offering significantly higher bandwidth compared to Cat 7. Cat 8 cables also utilize twisted pairs of copper wires, with improved shielding to reduce crosstalk and interference.
Speed and Bandwidth
-
- Cat 7 cables can support data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters. While Cat 7 cables provide impressive performance, they fall short of the speeds achievable with Cat 8 cables.
- Cat 8 cables boast speeds of up to 40 Gbps over distances of up to 30 meters. This makes them ideal for high-speed networking applications, such as data centers and enterprise environments where fast and reliable connectivity is essential.
Shielding
-
- Cat 7 cables typically feature shielding in the form of individually shielded pairs (S/FTP) or overall shielding (F/FTP). This shielding helps minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensures stable performance even in noisy environments.
- Cat 8 cables come with improved shielding, often in the form of fully shielded twisted pairs (S/FTP). This enhanced shielding provides superior protection against crosstalk and external interference, making Cat 8 cables highly reliable for demanding networking scenarios.
Compatibility
-
- Cat 7: Backward compatible with lower category cables, allowing for seamless integration into existing networks.
- Cat 8: While compatible with previous categories, Cat 8 cables are best utilized in environments where high-speed networking is paramount.
Cost Comparison
-
- Cat 8 cables are typically more expensive than Cat 7 cables due to their advanced specifications and performance capabilities.
- Cat 7 cables offer a balance between performance and cost, Cat 8 cables are the preferred choice for applications requiring high-speed, future-proof connectivity.
Certainly! Here’s the summary of the key features of Cat 7 and Cat 8
| Feature | Cat 7 Cable | Cat 8 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Bandwidth | Up to 600 MHz | Up to 2000 MHz |
| Shielding | Individually shielded pairs (S/FTP) or overall shielding (F/FTP) | Fully shielded twisted pairs (S/FTP) |
| Compatibility | Backward compatible with lower category cables (Cat 6, Cat 5e) | Backward compatible with lower category cables (Cat 6, Cat 5e) Requires compatible networking equipment for optimal performance |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically more expensive |
| Use Cases | Home networks, small businesses, residential installations | Data centers, server rooms, enterprise environments |
Making the Right Choice
In conclusion, the choice between Cat 7 and Cat 8 Ethernet cables boils down to your specific networking requirements and environment. If you prioritize speed and have relatively shorter distances to cover, Cat 8 cables offer unparalleled performance. On the other hand, Cat 7 cables provide a balance of speed and reach, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
FAQs
Are Cat 7 cables backward compatible?
Can I use Cat 8 cables for residential installations?
Do I need special equipment to use Cat 8 cables?
Are Cat 8 cables more difficult to install than Cat 7 cables?

Hey, I enjoyed reading your posts! You have great ideas. Are you looking to get resources about Data Mining or some new insights? If so, check out my website Webemail24