Contents
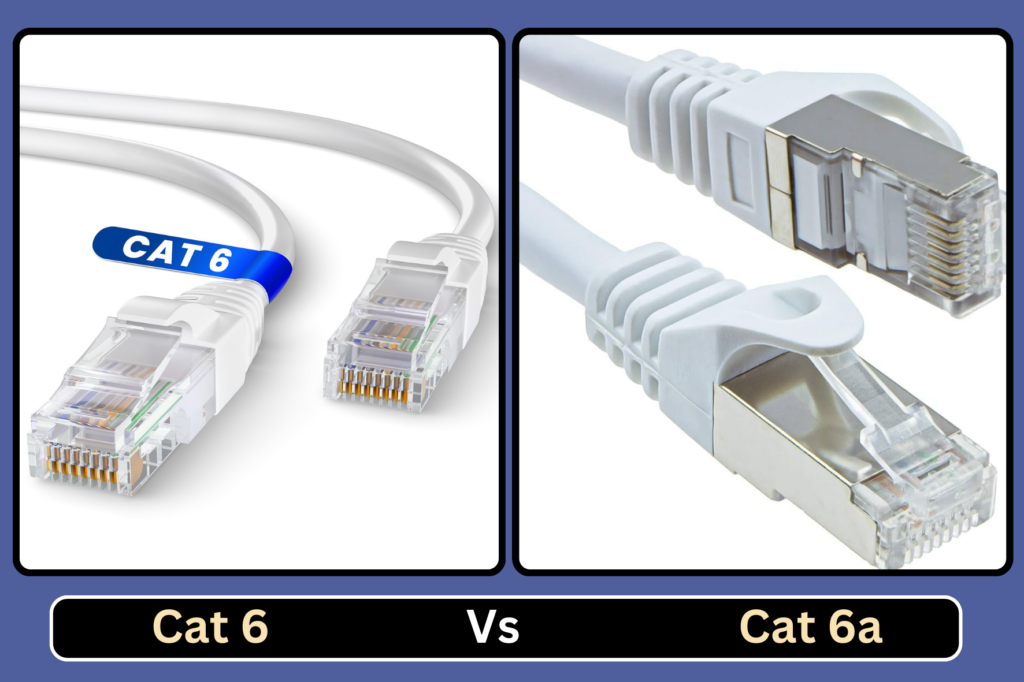
Difference Between Cat6 and Cat6a Cable
In the world of networking, the choice of cables can significantly impact performance, reliability, and future-proofing of your network infrastructure. Cat6 and Cat6a cables are two popular options, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is crucial for making informed decisions when setting up or upgrading a network.
What are Cat6 ethernet Cables?
Cat6 cables, short for Category 6 cables, are widely used in Ethernet networking. They are an improvement over their predecessor, Cat5e cables, offering higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds. Cat6 cables are designed to support data rates of up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps) over short distances of up to 55 meters, making them suitable for most residential and commercial networking needs.
Key Features of Cat6 ethernet Cables:
-
- Bandwidth: Cat6 cables typically support bandwidths of up to 250 MHz, allowing for faster data transmission and reduced latency.
- Performance: With their enhanced specifications, Cat6 cables are capable of delivering superior performance, especially in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Compatibility: Cat6 cables are backward compatible with older Ethernet standards such as Cat5 and Cat5e, ensuring seamless integration into existing network infrastructures.
- Cost: While Cat6 cables offer improved performance, they are generally more affordable than higher-grade options like Cat6a cables, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Pros & Cons of Cat6 ethernet Cables:
Pros of Cat6 Cables:
-
- Cost-Effective: Cat6 cables are generally more affordable than Cat6a cables, making them a budget-friendly option for many installations.
- High Performance: With support for data rates of up to 10 Gbps over short distances, Cat6 cables offer excellent performance for most residential and commercial networking needs.
- Backward Compatibility: Cat6 cables are backward compatible with older Ethernet standards, allowing for seamless integration into existing network infrastructures.
- Widespread Availability: Cat6 cables are widely available and commonly used, making them easy to find and purchase for network installations.
Cons of Cat6 Cables:
-
- Limited Reach: Cat6 cables are limited to shorter transmission distances of up to 55 meters for 10 Gbps speeds, which may not be suitable for larger installations.
- Less Future-Proofing: While Cat6 cables offer adequate performance for current needs, they may require upgrading in the future as network bandwidth demands increase.
What are Cat6a Cables?
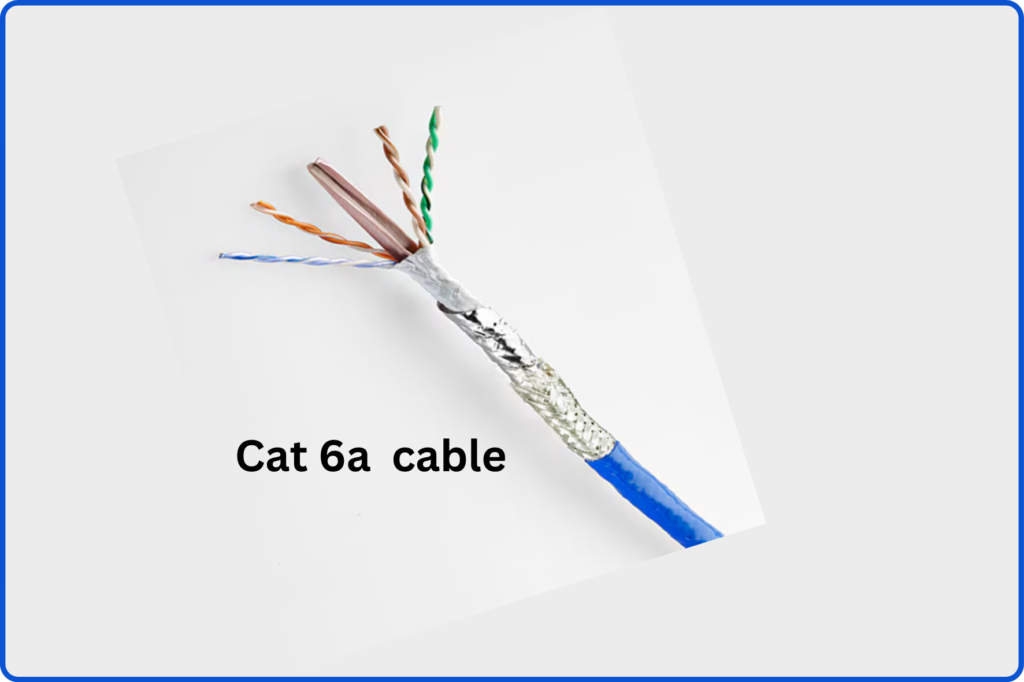
Cat6a cables, or Category 6a cables, are an advanced version of Cat6 cables, offering even higher performance and reliability. The “a” in Cat6a stands for augmented, indicating the augmented specifications compared to standard Cat6 cables. Cat6a cables are designed to support 10 Gigabit Ethernet over longer distances of up to 100 meters, making them ideal for demanding networking environments.
Key Features of Cat6a Cables:
-
- Enhanced Performance: Cat6a cables support higher data rates of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances, providing reliable connectivity for high-speed networking applications.
- Improved Shielding: Cat6a ethernet cables often feature better shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring stable performance in noisy environments.
- Future-Proofing: With their superior specifications, Cat6a cables offer better future-proofing for network upgrades and expansions, accommodating the increasing bandwidth demands of modern applications.
- Longer Reach: Cat6a ethernet cables can transmit data over distances of up to 100 meters without experiencing significant signal degradation, making them suitable for larger installations and structured cabling systems.
Pros & Cons of Cat6a Cables:
Pros of Cat6a Cables:
-
- High Performance: Cat6a cables support data rates of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances of up to 100 meters, providing superior performance for demanding networking applications.
- Enhanced Shielding: Cat6a cables often feature better shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring stable performance in noisy environments.
- Future-Proofing: With their superior specifications, Cat6a cables offer better future-proofing for network upgrades and expansions, accommodating increasing bandwidth demands.
- Longer Reach: Cat6a cables can transmit data over longer distances without experiencing significant signal degradation, making them suitable for larger installations and structured cabling systems.
Cons of Cat6a Cables:
-
- Higher Cost: Cat6a cables are generally more expensive than Cat6 cables due to their enhanced performance and specifications, making them less budget-friendly for some installations.
- Less Common: While Cat6a cables offer superior performance, they may be less commonly available compared to Cat6 cables, potentially limiting options for purchasing and installation.

Comparison Cat6 Vs.Cat6a Cable
Understanding the disparities between CAT6 and CAT6a cables is essential for selecting the most suitable option for your networking needs.
Construction
-
- CAT6: CAT6 cables typically consist of four twisted pairs of copper wire and utilize a thicker sheath compared to previous generations, providing better protection against crosstalk and interference.
- CAT6a: CAT6a cables boast a similar construction to CAT6 cables but feature additional shielding and thicker conductors, enabling them to support higher transmission speeds over longer distances.
Performance
-
- CAT6: CAT6 cables support Gigabit Ethernet speeds up to 1 Gbps and are suitable for most residential and commercial networking applications.
- CAT6a: CAT6a cables offer significantly higher performance, capable of supporting 10 Gigabit Ethernet speeds up to 10 Gbps. They excel in environments requiring high data throughput and minimal latency.
Bandwidth
-
- CAT6: CAT6 ethernet cables typically have a bandwidth capacity of 250 MHz, providing sufficient throughput for most networking tasks.
- CAT6a: CAT6a ethernet cables boast a higher bandwidth capacity of 500 MHz, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications and future-proofing your network infrastructure.
Cost
- CAT6: CAT6 ethernet cables are generally more cost-effective than CAT6a cables, making them a budget-friendly option for many users.
- CAT6a: CAT6a ethernet cables tend to be more expensive due to their enhanced performance and construction, but they offer superior long-term value for high-speed networking requirements.
Environmental Factors:
Consider the environmental conditions in which the cables will be installed. If your network is susceptible to electromagnetic interference or operates in a noisy environment, Cat6a cables with enhanced shielding may provide better reliability and stability.
Longevity:
Investing in Cat6a cables may offer better long-term benefits in terms of future upgrades and scalability, providing peace of mind and minimizing the need for costly re-cabling projects down the line.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Cat6 and Cat6a cables have their own strengths and are suitable for different networking requirements. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables allows you to make informed decisions based on your specific needs, budget, and performance expectations.