Contents
Difference between conductor and insulator
Conductors and insulators are fundamental concepts in the realm of physics and electrical engineering, playing pivotal roles in the functioning of various devices and systems. Understanding the disparity between these two types of materials is crucial for comprehending the behavior of electricity and its applications in everyday life.
What are conductors?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electric current. They have an abundance of free electrons within their structure, which can move freely in response to an applied electric field. This property makes conductors ideal for transmitting electricity efficiently. Metals, such as copper and aluminum, are common examples of conductors due to their high electron mobility.
How to identify a conductor:
-
- Conductivity: Check for materials with high electrical conductivity.
- Electron Mobility: Materials with free electrons are likely conductors.
- Examples: Metals such as copper, aluminum, and silver are common conductors.
Applications of Conductors
Conductors find applications in various fields due to their ability to facilitate the flow of electric current. Some common applications include:
-
- Electrical Wiring: Conductors like copper are extensively used in electrical wiring for buildings, homes, and industries. They serve as efficient channels for transmitting electricity from power sources to various electrical appliances and devices.
- Power Transmission: In power transmission systems, conductors play a crucial role in transmitting electricity over long distances from power plants to distribution centers and eventually to end-users. High-conductivity materials ensure minimal energy loss during transmission, maintaining the efficiency of the power grid.
- Electronic Circuits: Conductors are integral components of electronic circuits, where they provide paths for electric current to flow between different components such as resistors, capacitors, and semiconductor devices. They enable the functioning of electronic devices and systems, ranging from simple gadgets to complex computers and communication devices.
- Electric Motors and Generators: Conductors are essential components in electric motors and generators, where they form coils that interact with magnetic fields to produce mechanical motion or electrical energy. The conductivity of these coils ensures efficient energy conversion and optimal performance of the machines.
- Heating Elements: Certain conductive materials, such as nichrome wire, are used as heating elements in appliances like electric stoves, ovens, and space heaters. When electric current passes through these materials, they generate heat due to resistance, allowing for controlled heating applications.
- Electroplating: Conductors are employed in electroplating processes to coat metal objects with a thin layer of another metal. The object to be plated acts as the cathode, while a conductive material, often a metal conductor, serves as the anode. Electric current passing between the anode and cathode causes metal ions to deposit onto the surface of the object, resulting in a desired metallic coating.
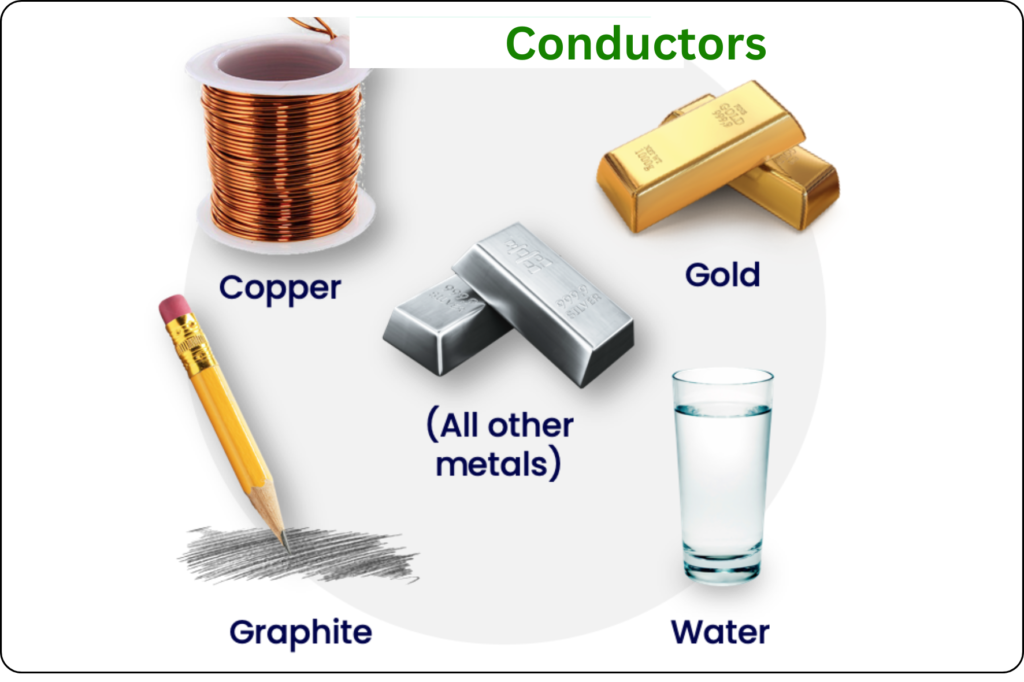
Some Examples of conductors?
Examples of conductors include:
-
- Copper: Widely used in electrical wiring and electronics due to its high conductivity and affordability.
- Aluminum: Commonly used in power transmission lines and electrical conductors for its good conductivity and lightweight properties
- Silver: Exhibiting the highest electrical conductivity among metals, silver is utilized in specialized applications such as electrical contacts and high-performance electronics.
- Gold: Though expensive, gold is valued for its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-end electrical connectors and circuitry.
- Iron: While not as conductive as copper or aluminum, iron is used in applications where its mechanical strength is advantageous, such as in electrical transformers and motors.
- Graphite: Known for its ability to conduct electricity along its layers, graphite is used in applications like electrodes, batteries, and lubricants.
- Brass: A mixture of copper and zinc, brass is used in electrical components, fittings, and connectors due to its conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Bronze: Another copper alloy, bronze is utilized in electrical components and machinery for its conductivity and durability.
- Carbon: Certain forms of carbon, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene, exhibit exceptional conductivity and are used in advanced electronic devices and materials.
- Mercury: A liquid metal at room temperature, mercury is used in some switches and electrical components due to its high conductivity and ability to flow and make electrical contact.
what are insulator?
Insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric current. Unlike conductors, insulators have few or no free electrons available for conduction. This property prevents the movement of electric charge through the material, making insulators ideal for isolating electrical components and preventing the occurrence of short circuits.
How to identify an insulator:
-
- Resistance: Look for materials with high electrical resistance.
- Electron Structure: Insulators typically have tightly bound electrons.
- Examples: Rubber, glass, and plastic are typical insulating materials.
Applications of insulators?
Insulators have a wide range of applications across various industries and technologies due to their ability to prevent the flow of electric current. Some common applications of insulators include:
- Electrical Insulation: Insulators are extensively used to isolate conductive components and prevent the flow of electric current in electrical systems. They are employed in wires, cables, and electrical equipment to prevent short circuits, electrical shocks, and unintended interactions between conductors.
- Power Distribution: Insulators play a critical role in power distribution systems, particularly in overhead power lines and electrical substations. They are used to support and insulate conductors, preventing electricity from leaking to the ground and ensuring the efficient transmission of power over long distances.
- High Voltage Equipment: Insulators are essential components in high voltage equipment such as transformers, switchgear, and circuit breakers. They help to isolate and protect sensitive components from electrical arcing, corona discharge, and other forms of electrical stress.
- Electronic Devices: Insulators are incorporated into electronic devices and circuitry to provide electrical isolation between components and circuits. They help to prevent signal interference, capacitance coupling, and other undesirable effects that can degrade the performance of electronic systems.
- Thermal Insulation: Certain insulating materials, such as foam, fiberglass, and thermal ceramics, are used for thermal insulation purposes. They help to minimize heat transfer and maintain temperature stability in buildings, appliances, industrial equipment, and transportation vehicles.
- Safety Equipment: Insulators are utilized in safety equipment such as insulating gloves, mats, and blankets for electrical workers and technicians. These insulating materials protect individuals from electrical hazards during maintenance, repair, and testing activities.
- Electronic Packaging: Insulators are used in electronic packaging and encapsulation to provide mechanical support, thermal management, and electrical insulation for semiconductor devices, integrated circuits, and electronic assemblies.
- Construction Materials: Insulating materials such as foam board, fiberglass insulation, and reflective barriers are employed in construction for thermal insulation, soundproofing, and moisture control in buildings and infrastructure projects.
Some Examples of Insulators?
Examples of insulators include:
-
- Rubber: Rubber is a common insulating material used in various applications due to its high resistance to electricity and flexibility.
- Plastic: Plastics such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), and PP (polypropylene) are widely used as insulators in electrical wiring, cables, and electronic devices.
- Glass: Glass is an excellent insulator due to its high electrical resistance and transparency. It is used in insulating windows, electrical insulators, and laboratory equipment.
- Ceramics: Ceramic materials, including porcelain and alumina, are used as insulators in high-temperature and high-voltage applications such as electrical insulators, spark plugs, and heating elements.
- Wood: Wood is a natural insulator commonly used in construction for its thermal and electrical insulating properties. It is used in building frames, doors, windows, and electrical poles.
- Air: Air is an effective insulator when trapped in enclosed spaces, such as in foam insulation, double-glazed windows, and vacuum insulation panels.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers, is widely used as thermal and acoustic insulation in buildings, appliances, and industrial equipment.
- Cork: Cork is a natural insulator with excellent thermal and acoustic properties. It is used in flooring, wall insulation, and as gaskets and seals in various applications.
- Porcelain: Porcelain insulators are commonly used in electrical transmission and distribution systems due to their high mechanical strength and resistance to electrical arcing.
- Mica: Mica is a mineral with excellent electrical insulation properties, commonly used as an insulating material in electrical equipment, capacitors, and heating elements.

Difference between conductor and insulator
| Characteristic | Conductors | Insulators |
|---|---|---|
| Flow of Electric Current | Facilitates the flow of electric current. | Resists the flow of electric current. |
| Electron Mobility | Electrons have high mobility. | Electrons have low mobility. |
| Band Structure | Valence and conduction bands overlap. | Large energy gap between bands. |
| Electric charge | Electric charge exists on the surface of conductors | Electric charges are absent in insulator. |
| Temperature Dependence | Conductivity may decrease with increasing temperature. | Less affected by temperature changes. |
| Usage in Electrical Systems | Used in electrical wiring, transmission lines, and electronic circuits. | Used for electrical insulation, wire insulation, and protective coatings. |
| Electrical Resistance | Low electrical resistance. | High electrical resistance. |
| Material Composition | Typically metals or materials with high electron conductivity. | Various materials including plastics, ceramics, and glass. |
| Examples | Copper, Iron, Steel, Silver, Gold, Aluminum, Mercury, etc | Rubber, glass, plastic, wood, air, fiber glass, mica, etc |

