Contents
- 1 Ethernet Cable Vs Network Cable:
- 1.1 What is an Ethernet Cable?
- 1.2 What is a Network Cable?
- 1.3 Differences Between Ethernet and Network Cables:
- 1.4 Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs:
- 1.5 Conclusion: Making the Right Choice:
- 1.6 FAQ
- 1.6.1 Q: What is the difference between Ethernet and network cables?
- 1.6.2 Q: What are the types of Ethernet cables available?
- 1.6.3 Q: What are the types of network cables besides Ethernet?
- 1.6.4 Q: How do I choose the right cable for my networking needs?
- 1.6.5 Q: Can I use Ethernet cables for other types of networking connections?
- 1.6.6 Q: What are the benefits of using fiber optic cables over Ethernet cables?
Ethernet Cable Vs Network Cable:
Ethernet and network cables are fundamental components of wired networking systems. They facilitate the transfer of data between devices within a network, such as computers, routers, switches, and printers. Ethernet cables, a subset of network cables, specifically refer to cables designed for Ethernet networking protocols. Network cables, on the other hand, encompass a broader category, including various types of cables used for networking purposes, such as Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables. Understanding the distinctions between Ethernet and network cables is essential for effectively setting up and maintaining network infrastructures.

What is an Ethernet Cable?
An Ethernet cable is a type of network cable specifically designed to connect devices within a local area network (LAN). It’s commonly used to establish a wired connection between devices such as computers, routers, switches, and other networking equipment. Ethernet cables come in various categories, including Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7, each offering different levels of performance and speed.
Types of Ethernet Cables:
Ethernet cables are classified into different types based on their performance characteristics and capabilities. These types include:
Cat5:
This is an entry-level Ethernet cable suitable for basic networking needs. It supports data transfer speeds of up to 100 Mbps.
Cat5e:
An enhanced version of Cat5, Cat5e offers better performance and higher speeds, supporting data rates of up to 1 Gbps.
Cat6:
Designed for Gigabit Ethernet networks, Cat6 cables can handle higher data transmission speeds and offer improved performance compared to Cat5e.
Cat6a:
Cat6a cables support 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks, making them suitable for high-speed applications and environments where maximum bandwidth is required.
Cat7:
Cat7 cables are designed for ultra-fast networking environments. They support speeds of up to 100 Gbps over short distances and feature improved shielding for reduced signal interference.

Each type of Ethernet cable has its own specifications and is suitable for different networking requirements.
What is a Network Cable?
On the other hand, the term “networking cable” is a broader category that encompasses various types of cables used in networking applications. While Ethernet cables are a subset of network cables, other types such as coaxial cables, fiber optic cables, and twisted pair cables also fall under this category.
Types of Network Cables:
In addition to Ethernet cables, there are other types of network cables used in networking applications. These include:
Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables are commonly used for cable television (TV) and internet connections. They consist of a central copper conductor surrounded by insulating material and a metallic shield.
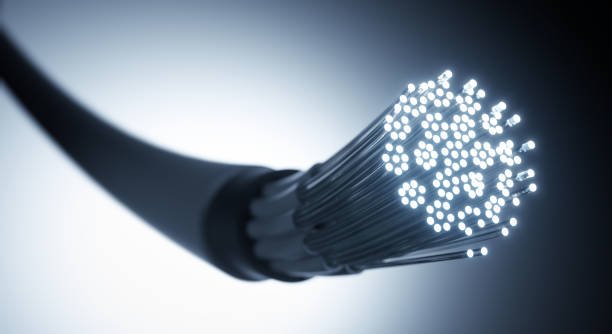
Fiber Optic Cables:
Fiber optic cables use light signals to transmit data and are known for their high-speed data transmission capabilities over long distances. They are often used in telecommunications and data networking applications.
Twisted Pair Cable:
Twisted pair cables, such as Ethernet cables, consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together. They are widely used in Ethernet networks and telecommunications for their cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Coaxial, fiber optic and Twisted pair cables offer different advantages and are chosen based on factors such as data transmission speed, distance, and environmental considerations.
Differences Between Ethernet and Network Cables:
While Ethernet cables are a type of network cable, there are differences between the two terms. Ethernet cables specifically refer to cables used for Ethernet networking protocols, primarily utilizing twisted pair copper wires. On the other hand, network cables encompass a broader range of cable types used in networking applications, including Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables. Ethernet cables are typically used for local area networks (LANs) and are designed to support Ethernet communication standards, while network cables may include various cable types used for different networking purposes.
Key Differences:
Scope:
Ethernet cables are a subset of network cables, focusing on cables used specifically for Ethernet networking standards. Network cables cover a wider range of cable types used for various networking purposes, including Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables.
Usage:
Ethernet cables are primarily used for local area networks (LANs) and are commonly found in office and home networking environments. Network cables, including Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables, are used in a variety of networking applications, ranging from LANs to wide area networks (WANs) and telecommunications infrastructure.
Materials and Construction:
Ethernet cables typically consist of twisted pair copper wires encased in an outer sheath, with different categories offering varying levels of performance and speed. Network cables may utilize different materials and construction methods depending on the cable type, such as coaxial cables with a central conductor surrounded by insulating material and a metallic shield, or fiber optic cables using glass or plastic fibers for data transmission through light signals.
Performance and Speed:
Ethernet cables, especially higher categories like Cat6 and Cat6a, offer faster data transmission speeds and better performance compared to lower categories like Cat5e. Other network cable types like fiber optic cables can provide even higher data transmission speeds and longer transmission distances compared to traditional Ethernet cables.
Applications:
Ethernet cables are commonly used for connecting devices within a LAN, such as computers, printers, routers, and switches, to facilitate data transfer and communication. Network cables, including Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables, serve various applications beyond LANs, including internet connections, cable television (TV), telecommunications networks, and data centers.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs:
When selecting the appropriate cable for your networking needs, it’s essential to consider factors such as:
Required data transmission speed:
Determine the speed and bandwidth requirements of your network to choose a cable that can support them.
Distance:
Consider the distance between network devices and select a cable type that can accommodate the required distance without signal degradation.
Compatibility:
Ensure compatibility with your existing networking equipment, including routers, switches, and network interface cards (NICs).
Future scalability:
Consider potential future upgrades or expansions of your network infrastructure and choose a cable type that allows for scalability and flexibility. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the right cable to optimize your network performance and reliability.
Also Read: Data Cable vs Ethernet Cable
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice:
Choosing between Ethernet and network cables depends on your specific networking requirements and considerations. By understanding the differences between the types of cables available, considering factors such as speed, distance, and compatibility, and evaluating your future networking needs, you can make the right choice for your network infrastructure. Whether you opt for Ethernet cables for standard LAN setups or select other network cable types like coaxial or fiber optic cables for specialized applications, making an informed decision ensures efficient and reliable data transmission within your network.
FAQ