Contents
Ethernet Splitter vs Switch
In the realm of networking, two devices frequently spark confusion among users: the Ethernet Splitter and the Ethernet Switch. While they may seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different network setups. To navigate the networking landscape effectively, it’s crucial to comprehend the disparities between these two components.

What is an Ethernet splitter?
An Ethernet splitter is a passive networking device designed to divide a single Ethernet connection into multiple ports, allowing multiple devices to share the same network connection simultaneously. It operates by splitting the incoming Ethernet signal into two or more signals, enabling data transmission to multiple devices without the need for additional network infrastructure. Ethernet splitters are typically used in small-scale setups where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over advanced networking capabilities. They are commonly employed in home networks or small office environments to expand connectivity options without the need for a larger switch. The Two types of Ethernet Splitter one is powered and other is unpowered ethernet spliter.
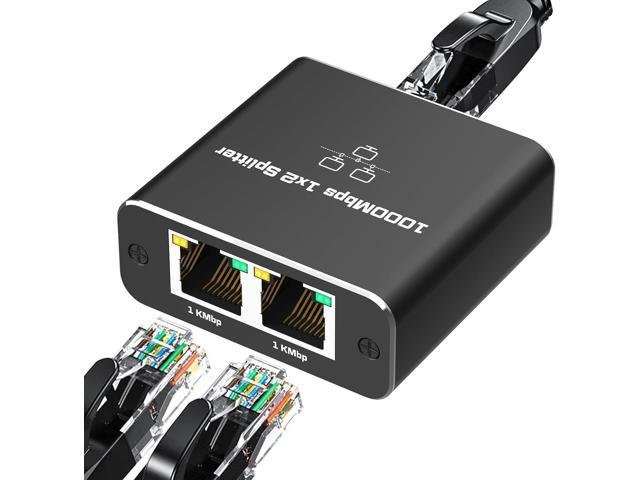

Powered Ethernet Splitters:
Powered Ethernet Splitters also known as active splitters, powered Ethernet splitters have following charactristics:
-
- Require external power source.
- Active signal management
- Ensuring efficient data transmission to connected devices.
- Allowing multiple devices to connect to the network simultaneously.
- Signal regeneration or amplification.
- Suitable for larger networks.
- Higher cost.
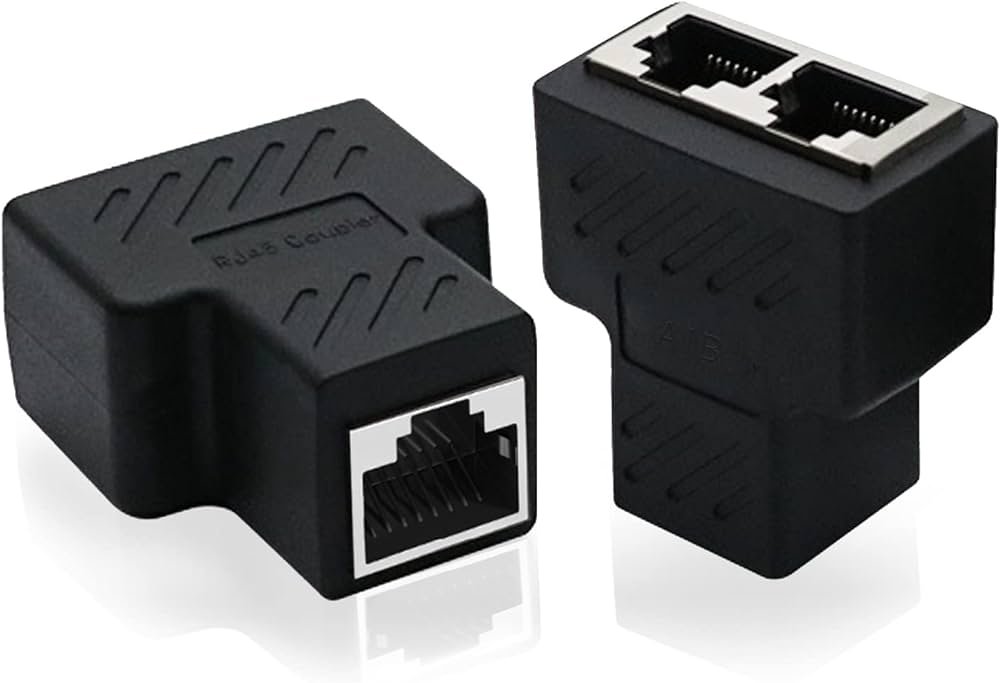

Unpowered Ethernet Splitters:
Unpowered Ethernet Splitters also referred to as passive splitters, unpowered Ethernet splitters have following characteristics:
-
- No external power required.
- Passive signal splitting.
- Work by splitting the incoming Ethernet signal into multiple output ports.
- Only one connection can be utilized at a time with the splitter.
- Cost-effective solution.
- Limited additional features.
- Suitable for small-scale setups
What is an Ethernet Switch?
An Ethernet switch is a networking device that connects multiple devices within a local area network (LAN). It operates by receiving data packets from one device and then forwarding them to the appropriate destination device based on the MAC (Media Access Control) address. Unlike hubs or splitters, which simply broadcast data to all connected devices, a switch intelligently manages traffic, optimizing the flow of data and improving network efficiency. Ethernet switches come in various configurations, offering different numbers of ports to accommodate varying network sizes and requirements. They are widely used in homes, offices, data centers, and enterprise environments to facilitate reliable and high-speed communication between devices.
 The ethernet switch with 8 ports, POE Port, Gigabit Port. Vector illustration.
The ethernet switch with 8 ports, POE Port, Gigabit Port. Vector illustration.
All Ethernet switches possess the following characteristics:
-
- Ethernet switches function at Layer 2, handling MAC addresses within LANs.
- They employ packet switching for forwarding data frames using MAC addresses.
- Switches learn MAC addresses dynamically by observing incoming frame source addresses.
- Maintaining a forwarding table, switches map MAC addresses to reachable ports.
- Frames are forwarded based on the switch’s table, ensuring precise destination delivery.
- Switches distribute broadcast frames to all ports except the source, and multicast frames only to relevant ports.
- Each port on a switch creates a distinct collision domain, enhancing network efficiency.
- Most switches support full-duplex communication, enabling simultaneous data transmission and reception.
- Many switches offer VLAN support, facilitating network segmentation for improved security and managemen
- Advanced switches may include Quality of Service (QoS) features, prioritizing certain traffic for optimized performance
The Two types of Ethernet switch one is Unmanaged and other is managed ethernet switch.
What is an unmanaged Ethernet switch?
An unmanaged Ethernet switch is a type of networking device that operates without the need for manual configuration or management. It typically features a plug-and-play design, allowing it to automatically detect and connect devices within a local area network (LAN) without requiring user intervention. Unmanaged switches are straightforward to set up and are ideal for small-scale networks or environments where simplicity is prioritized over advanced management features. They lack the capabilities for remote monitoring, configuration, or traffic prioritization found in managed switches, making them suitable for basic networking needs.
What is an managed Ethernet switch?
A managed Ethernet switch is a networking device that offers advanced features and capabilities for network administrators to monitor, configure, and optimize network performance. Unlike unmanaged switches, managed switches provide extensive control over network operations, allowing administrators to customize settings, prioritize traffic, and implement security measures. Managed switches typically offer features such as VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS), port mirroring, and SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) for remote monitoring and management. They are commonly used in larger networks, data centers, and enterprise environments where fine-tuning network settings and maximizing efficiency are priorities.
Also Read: Ethernet Cable vs. Network Cable
Ethernet splitter vs Ethernet switch
Ethernet splitter and Ethernet switchare both networking devices used to connect multiple devices to a network, but they have distinct differences:
Ethernet Splitter:
-
- Functionality: Splits a single Ethernet connection into multiple ports, allowing devices to share the same network connection.
- Operation: Operates passively, without actively managing data traffic.
- Limitation: Only one connection can be used at a time with the splitter.
- Suitability: Ideal for small-scale setups where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over advanced networking capabilities.
Ethernet Switch:
-
- Functionality: Connects multiple devices within a network and intelligently manages data traffic.
- Operation: Actively manages data traffic, directing data packets only to the intended destination devices.
- Advantages: Supports simultaneous connections from multiple devices and offers features like VLANs, QoS, and port mirroring.
- Suitability: Suitable for larger networks, data centers, and enterprise environments where network efficiency and scalability are crucial.
When considering the comparison between Ethernet splitters and Ethernet switches, it’s evident that Ethernet switches emerge as the preferred choice while Ethernet splitters present limitations. Specifically, unpowered Ethernet splitters not only lack utility but also impede network performance for connected devices. Conversely, Ethernet switches play a vital role in Ethernet networking, enabling efficient simultaneous communication between devices and overcoming length restrictions inherent in copper Ethernet cables.
These limitations arise from the resistance induced by copper, particularly over longer distances and in higher temperatures. Ethernet switches effectively mitigate these issues by renewing the signal, extending cable runs, and providing additional ports. Even seemingly minor powered “splitters” are essentially Ethernet switches disguised as splitters, making them superior options.
In conclusion, Ethernet switches are indispensable for optimizing network performance and are thus a fundamental requirement in any Ethernet network setup. When designing your Ethernet network, it’s essential to prioritize high-quality and high-performing equipment, with Ethernet switches being a necessary component.