Contents
- 1 Introduction to Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
- 2 Fusion Splicing:
- 3 Mechanical Splicing:
- 4 Fusion splicing vs mechanical splicing
- 5 Fiber Optic Splicing Tools and Equipment
- 6 Best Practices for Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
- 7 Importance of Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
- 8 Conclusion: Ensuring Reliable Fiber Optic Connections
Introduction to Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
Fiber optic cable splicing is a critical process in telecommunications infrastructure maintenance and installation. It involves joining of two fiber optic cables to create a continuous pathway for data transmission. Proper splicing ensures minimal signal loss and maximum efficiency in fiber optic networks. In the world of modern communication, where speed and reliability are paramount, understanding the basics of fiber optic cable splicing is essential. This introductory guide aims to demystify the process and highlight its importance in maintaining robust telecommunications networks.
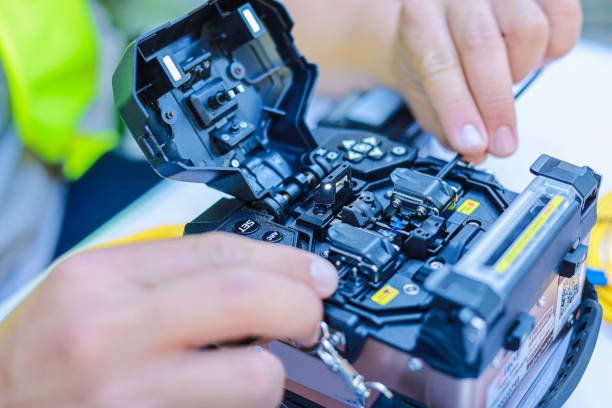

There are two main types of fiber optic cable splicing: fusion splicing and mechanical splicing. Both fusion and mechanical splicing techniques are crucial for maintaining efficient data transmission in fiber optic networks, with each method offering its own advantages and suitability for different applications.
Fusion Splicing:
Fusion splicing involves precisely aligning and permanently joining two optical fibers using a fusion splicer. This method melts the ends of the fibers together to create a seamless connection. Fusion splicing is typically used for permanent installations due to its reliability and low signal loss.
Fusion Splicing: Step-by-Step Guide
Fusion splicing, the gold standard in the industry, involves precisely aligning and permanently joining fiber optic cables. Here’s a brief rundown of the process:
Step 1:- Clean and Prepare the Fiber Ends
-
- Before splicing, the protective coatings surrounding the fiber ends must be removed to expose the bare glass.
- This process ensures that there are no contaminants present that could interfere with the fusion process.
- Cleaning the fiber ends meticulously is essential to achieve optimal fusion and minimize signal loss.
Step 2:- Align the Fibers Using a Fusion Splicer
-
- A fusion splicer is a specialized device used to precisely align the fiber ends with micrometer-level accuracy.
- This alignment is crucial for ensuring that the cores of the fibers are perfectly aligned, minimizing any loss of signal strength at the splice point.
- The fusion splicer utilizes advanced optics and alignment algorithms to achieve this precise alignment.
Step 3:- Apply Heat to Melt and Fuse the Fibers Together
-
- Once the fibers are aligned, the fusion splicer applies heat to the fiber ends to melt them together.
- This heat source can be generated by a controlled arc of electricity or a laser beam, depending on the type of fusion splicer used.
- The melted fibers fuse together, creating a seamless connection that allows light to pass through without significant loss.
Step 4:- Protect the Splice
-
- After fusion, it’s essential to protect the delicate splice point from any potential damage.
- This is typically done by encasing the splice in a splice sleeve or heat shrink tubing.
- These protective materials provide mechanical strength and environmental protection, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the spliced connection.
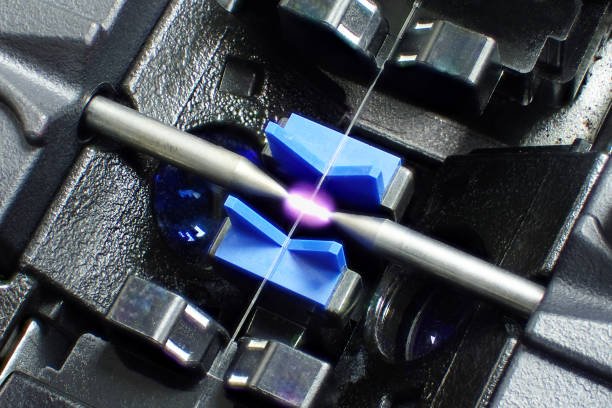
By following these steps meticulously, technicians can perform fusion splicing with precision and confidence, creating strong and durable connections essential for modern fiber optic networks.
Mechanical Splicing:
Mechanical splicing, on the other hand, involves aligning the fibers within a mechanical splice holder and securing them with a precision clamp mechanism. While not as permanent as fusion splicing, mechanical splicing offers a quicker solution and can be used for temporary connections or emergency repairs.
Mechanical Splicing: Step-by-Step Guide
Mechanical splicing provides a quicker alternative to fusion splicing, particularly useful for temporary or emergency repairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to mechanical splicing:
Step1:- Clean and Cleave the Fiber Ends
-
- Just like with fusion splicing, cleanliness is crucial for mechanical splicing. After cleaning the fiber ends meticulously, a fiber cleaver is used to ensure precise and perpendicular cuts.
- This step ensures that the fiber ends are smooth and flat, facilitating optimal alignment and contact during the splicing process.
Step 2:- Insert the Fibers into a Mechanical Splice Holder:
-
- The mechanical splice holder plays a key role in the splicing process by precisely positioning the fibers for optimal alignment and contact.
- This holder ensures that the fibers are held securely in place during the splicing process, minimizing any potential movement that could affect the quality of the splice.
Step3:- Secure the Fibers Using a Precision Clamp Mechanism:
-
- Once the fibers are inserted into the mechanical splice holder, a precision clamp mechanism is employed to apply controlled pressure.
- This pressure ensures a tight and secure connection between the fibers, crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing loss during data transmission.
Step 4:- Inspect the Splice:
-
- After securing the fibers, it’s essential to visually inspect the splice to ensure proper alignment and cleanliness.
- Any debris or imperfections in the splice can lead to signal loss, so it’s crucial to verify that the splice is clean and well-aligned.
- By conducting a thorough inspection, technicians can identify and address any issues before finalizing the splicing process, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the connection.
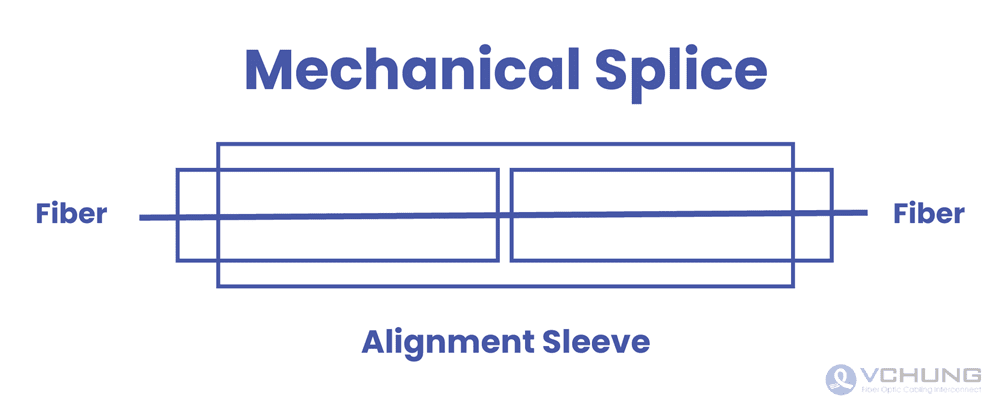
In summary, mechanical splicing offers a fast and effective solution for temporary or emergency repairs in fiber optic networks. By following these steps meticulously, technicians can perform mechanical splicing with confidence, ensuring reliable connectivity and minimal disruption to communication services.
Fusion splicing vs mechanical splicing
Fusion splicing and mechanical splicing are two common methods used in fiber optic cable termination, each with its own advantages and applications:
Fusion Splicing:
-
- Method: Fusion splicing involves precisely aligning and permanently joining the fiber optic cables by melting their ends together using a fusion splicer.
- Advantages: Fusion splicing typically results in lower insertion loss and higher tensile strength compared to mechanical splicing. It provides a permanent and reliable connection that is resistant to environmental factors.
- Applications: Fusion splicing is often preferred for permanent installations where low loss and high reliability are crucial, such as in long-haul telecommunications networks or data centers.
Mechanical Splicing:
-
- Method: Mechanical splicing involves aligning and securing the fiber optic cables using mechanical splice holders and precision clamp mechanisms.
- Advantages: Mechanical splicing is quicker and more cost-effective than fusion splicing, making it suitable for temporary or emergency repairs. It also does not require expensive equipment like fusion splicers.
- Applications: Mechanical splicing is commonly used for temporary connections, emergency repairs, or in situations where fusion splicing may not be practical or feasible due to time or budget constraints.
In summary, while fusion splicing offers superior performance and reliability for permanent installations, mechanical splicing provides a faster and more economical solution for temporary or emergency splicing needs. The choice between the two methods depends on factors such as installation requirements, budget constraints, and the desired level of performance and reliability.
Fiber Optic Splicing Tools and Equipment
To perform fiber optic cable splicing effectively, you’ll need a few essential tools and equipment:
-
- Fusion Splicer: For precision alignment and fusion of optical fibers.
- Fiber Cleaver: To achieve clean and perpendicular cuts of fiber ends.
- Splice Sleeves or Heat Shrink Tubing: For protecting and reinforcing the spliced area.
- Mechanical Splice Holder: To position and secure fibers for mechanical splicing.
- Precision Clamp: For applying controlled pressure during mechanical splicing.
- Fiber Optic Inspection Microscope: For detailed inspection of splices to ensure quality and cleanliness.
Best Practices for Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
Implementing best practices is essential for achieving optimal results in fiber optic cable splicing. Here are some key best practices to follow:
-
- Ensure Cleanliness: Maintaining cleanliness throughout the splicing process is paramount. This includes cleaning the fiber ends, work area, and splicing equipment to prevent contamination and ensure proper fusion or alignment.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for splicing equipment setup, operation, and maintenance. This ensures that the equipment functions correctly and produces reliable splices.
- Perform Regular Maintenance and Calibration: Regularly inspect and calibrate splicing tools and equipment to ensure consistent performance. This includes checking fusion splicer electrodes, cleaver blades, and other components for wear and tear.
- Conduct Quality Inspections: After splicing, conduct thorough quality inspections to verify signal integrity and splice quality. Use fiber optic inspection microscopes to examine the splices for proper alignment and cleanliness.
- Train Personnel: Provide comprehensive training to personnel involved in fiber optic cable splicing. Proper training ensures that technicians understand and follow best practices, leading to high-quality splices and reliable network performance.
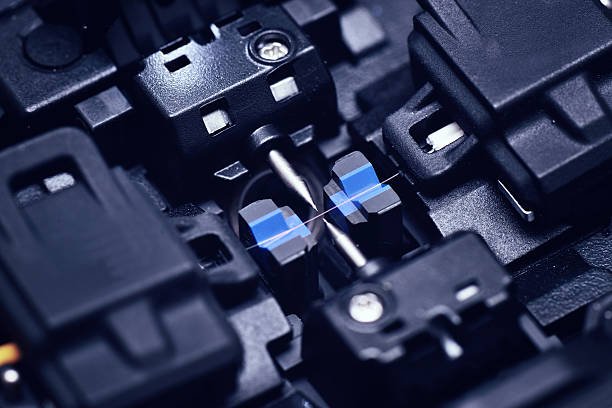
By adhering to these best practices, technicians can perform fiber optic cable splicing with confidence, ensuring efficient data transmission and maintaining the integrity of telecommunications networks.
Importance of Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
Fiber optic cable splicing is essential for seamless data transmission by establishing connections between optical fibers. It is crucial in telecommunications, internet services, and networking infrastructure. Splicing enables the creation of long-distance links without signal degradation, ensuring reliable communication. By joining optical fibers effectively, splicing maintains signal integrity over vast distances. This process plays a pivotal role in supporting the efficiency and reliability of modern communication networks. In essence, fiber optic cable splicing is indispensable for enabling efficient and uninterrupted data transmission in various industries and applications.
Conclusion: Ensuring Reliable Fiber Optic Connections
In the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunications, the demand for high-speed, reliable connectivity continues to grow. By mastering the art of fiber optic cable splicing and adhering to best practices, technicians can play a vital role in ensuring seamless data transmission and connectivity for businesses and consumers alike. Whether employing fusion or mechanical splicing methods, attention to detail, proper equipment, and rigorous quality control are essential for maintaining robust fiber optic networks.