Contents
- 1 How To Use an Ammeter To measure Current
- 2 What is an Ammeters?
- 3 Types of Ammeters
- 4 How to Use an Ammeter: Step-by-Step Guide
- 5 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 6 Applications of Ammeters
- 7 Benefits of Using an Ammeter
- 8 Tips for Efficient Ammeter Usage
- 9 Advanced Ammeter Techniques
- 10 Comparing Ammeters with Other Instruments
- 11 Future Trends in Ammeter Technology
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- 14 What is the difference between an ammeter and a multimeter?
- 15 Can I use an ammeter to measure both AC and DC current?
- 16 How do I know if my ammeter is accurate?
- 17 What should I do if my ammeter is showing unusual readings?
- 18 Is it safe to use an ammeter on live circuits?
How To Use an Ammeter To measure Current
Welcome to the ultimate guide on how to use an ammeter! Whether you’re a seasoned electrician or a DIY enthusiast, understanding how to effectively utilize an ammeter is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues, ensuring safety, and maintaining equipment. In this article, we’ll search into the fundamentals of ammeters, step-by-step procedures on their usage, common FAQs, and expert tips to enhance your proficiency.
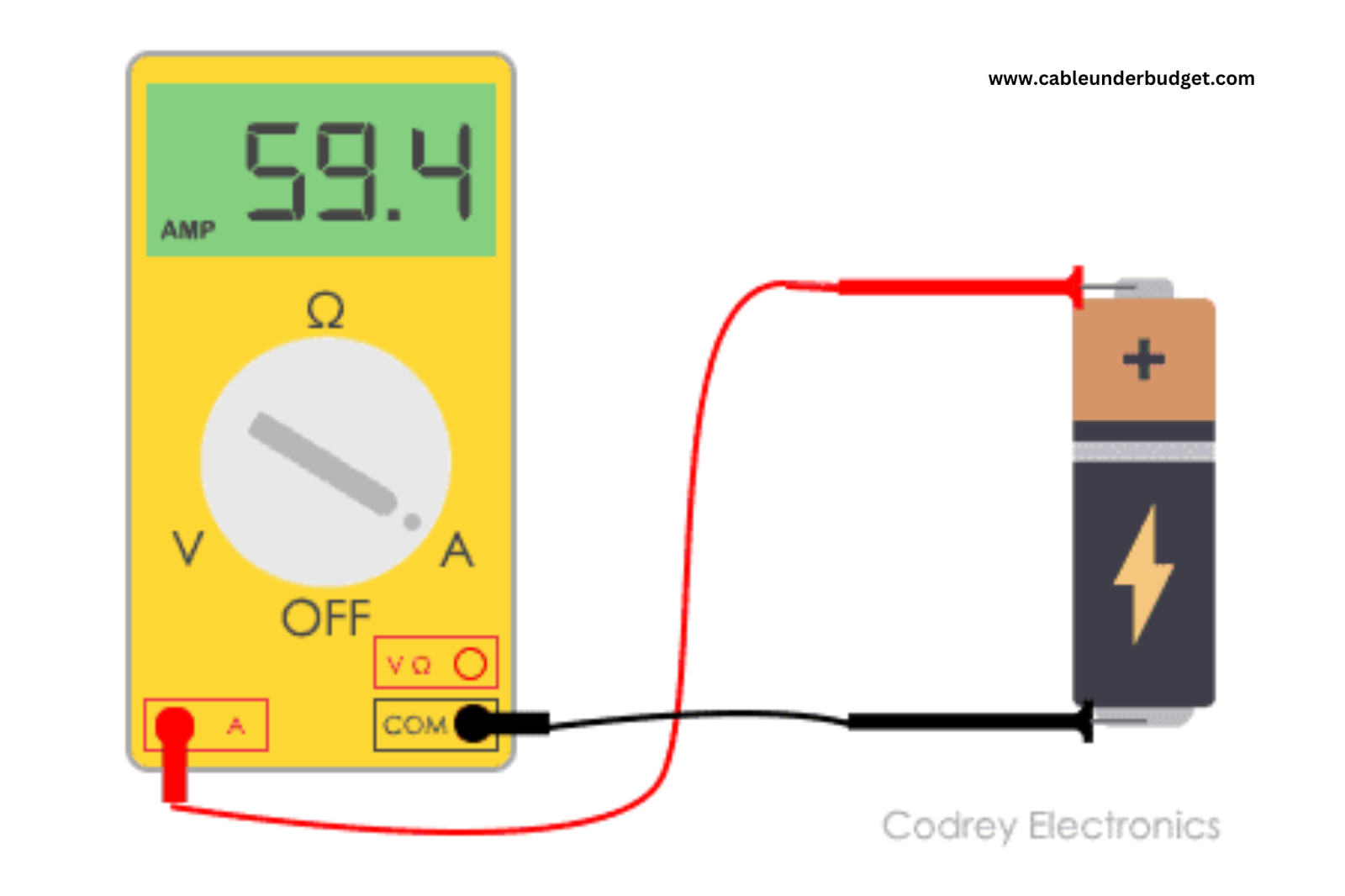
What is an Ammeters?
Ammeters are essential tools in electrical engineering, allowing the measurement of electrical current flow within a circuit. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, understanding how to use an ammeter is fundamental for troubleshooting electrical systems and ensuring safety.
Types of Ammeters
There are two main types of ammeters: analog and digital.
Analog ammeters utilize a needle or pointer to indicate current readings on a scale,
Digital ammeters display numerical values digitally.

Both types have their advantages and are suitable for various applications.
Understanding the Basics
Before using an ammeter, it’s crucial to understand basic concepts such as current measurement units (amps), circuit connections, and the principles of series circuitry. Ammeters are typically connected in series with the circuit under test to measure the current flowing through it accurately.
Precautions Before Using an Ammeter
Safety should always be a top priority when working with electrical systems. Before using an ammeter, ensure that you’re familiar with safety measures such as wearing appropriate protective gear and turning off power to the circuit. Additionally, double-check the setup to avoid any potential hazards.
How to Use an Ammeter: Step-by-Step Guide
Using an ammeter effectively requires careful attention to detail and adherence to proper procedures. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you use an ammeter correctly:
- Select the Right Ammeter: Before using an ammeter, ensure that you have the appropriate type for your application. Consider factors such as the expected current range and whether you need an analog or digital ammeter.
- Safety Precautions: Always prioritize safety when working with electrical equipment. Wear appropriate protective gear, and make sure the circuit you’re working on is de-energized to prevent accidents.
- Prepare the Circuit: Before connecting the ammeter, ensure that the circuit is properly set up for measurement. This may involve removing any components that could interfere with the measurement or adjusting the circuit configuration as needed.
- Connect the Ammeter in Series: To measure current accurately, connect the ammeter in series with the circuit under test. This means interrupting the circuit and placing the ammeter in the path of current flow. Follow the polarity markings on the ammeter to ensure correct orientation
- Turn on the Circuit: Once the ammeter is connected, you can turn on the circuit to allow current to flow through the ammeter. Be prepared to take readings promptly to minimize any potential safety risks.
- Read the Current: Observe the display on the ammeter to read the current flowing through the circuit. Analog ammeters typically use a pointer or needle to indicate current on a scale, while digital ammeters provide numerical readings directly on a digital display.
- Interpret the Reading: After taking the reading, interpret the displayed value to understand the current flow in the circuit. Pay attention to the units of measurement (usually in amperes or milliamperes) and compare the reading to expected values for the circuit.
- Record the Measurement: If necessary, record the measured current value for future reference or documentation. Note any relevant details about the circuit conditions or measurement setup that may affect the interpretation of the reading.
- Disconnect the Ammeter: Once you’ve completed the measurement, safely disconnect the ammeter from the circuit. Turn off the circuit power if it was turned on and ensure that all connections are secure before proceeding.
- Store the Ammeter Properly: After use, store the ammeter in a safe and secure location, taking care to protect it from damage. Follow any manufacturer recommendations for storage conditions to maintain the ammeter’s performance and longevity.
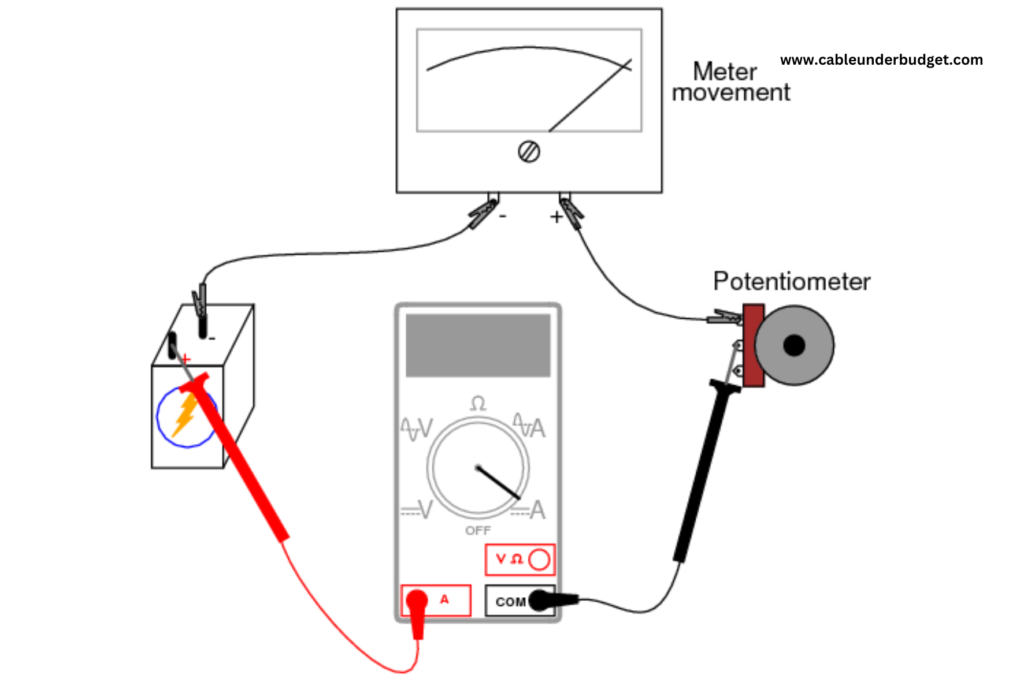
By following these steps, you can use an ammeter effectively and safely for measuring electric current in various electrical circuits. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult the user manual or seek professional guidance if you encounter any uncertainties.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is critical to ensure accurate measurements and prevent damage to the ammeter. These include overloading the ammeter with excessive current, using incorrect connections, and neglecting safety precautions. Be vigilant and double-check everything before taking measurements.
Applications of Ammeters
Ammeters have various applications, including electrical troubleshooting, circuit testing, and monitoring current consumption. Whether you’re diagnosing faults in a circuit or verifying the performance of electrical devices, an ammeter is an indispensable tool.
Benefits of Using an Ammeter
The benefits of using an ammeter are numerous. From its accuracy in measuring current to its efficiency in troubleshooting electrical problems, an ammeter is a valuable tool for anyone working with electrical systems. By using an ammeter correctly, you can save time and ensure the safety of your projects.
Tips for Efficient Ammeter Usage
To get the most out of your ammeter, follow these tips for efficient usage. Perform regular calibration checks to maintain accuracy, and handle the ammeter with care to avoid damage. Proper storage when not in use can also help prolong its lifespan and performance.
Advanced Ammeter Techniques
For more advanced applications, there are specialized techniques for using an ammeter. These include measuring AC current using RMS (root mean square) values and using clamp meters for non-contact current measurement. These advanced techniques expand the capabilities of an ammeter for various scenarios.
Comparing Ammeters with Other Instruments
While ammeters are essential for measuring current, they’re just one part of a complete set of electrical instruments. Comparing ammeters with other instruments such as voltmeters (for measuring voltage), Multimeter and ohmmeters (for measuring resistance) can provide a holistic view of the electrical system under test.
Future Trends in Ammeter Technology
As technology continues to advance, so too does the field of ammeter technology. Future trends include advancements in digital displays for greater readability and integration with smart devices for remote monitoring and control. These developments aim to make ammeters more user-friendly and versatile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing how to use an ammeter is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. By understanding the basics, following safety precautions, and using the ammeter correctly, you can ensure accurate measurements and efficient troubleshooting. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, mastering the use of an ammeter is a valuable skill that can save time, prevent accidents, and improve overall project outcomes.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between an ammeter and a multimeter?
Can I use an ammeter to measure both AC and DC current?
How do I know if my ammeter is accurate?
What should I do if my ammeter is showing unusual readings?
Is it safe to use an ammeter on live circuits?

