Contents
Introduction to LAN & Ethernet Cables
LAN (Local Area Network) and Ethernet cables are essential components of modern networking infrastructure, enabling the seamless transmission of data within and between networks. Understanding the disparity between these cables is crucial for optimizing network performance and efficiency.

Meaning of Local Area Networks (LANs):
Local Area Networks (LANs) are networks that connect devices within a confined geographical area such as homes, offices, or campuses. They are designed to serve a limited geographic area, allowing connected devices to communicate and share resources efficiently. LANs are commonly used in homes and businesses to facilitate tasks such as file sharing, printer sharing, and internet connectivity among devices like computers, printers, servers, and smartphones.
Origin of the Term LAN:
The term “LAN” emerged in the early days of networking to describe networks that covered a small or local area, in contrast to larger-scale networks like wide area networks (WANs) or metropolitan area networks (MANs). It reflects the localized nature of these networks, where devices are physically close to each other, enabling faster communication and resource sharing.
Also Read: Ethernet Cable vs. Network Cable
Difference Between LAN and Ethernet:
LAN refers to the entire network infrastructure within a limited geographic area, encompassing various networking technologies such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or Token Ring. Ethernet, on the other hand, specifically refers to the technology used for communication within a LAN. While LAN defines the scope of the network, Ethernet defines the standards and protocols for data transmission within that network.
What is Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects devices within a specific geographic area, enabling communication and resource sharing among them. LANs are typically confined to a single building or campus, providing high-speed connectivity for local devices.
Understanding Ethernet:
Ethernet is a widely used networking technology for connecting devices within a LAN. It defines standards for the physical layer (e.g., wiring and connectors) and the data link layer (e.g., frame format and access methods) of the OSI model. Ethernet enables devices to communicate with each other using common protocols and standards, facilitating efficient data exchange within the LAN.

Key Differences between LAN and Ethernet:
When it comes to LAN the key differences are:
-
- Scope:
-
- LAN (Local Area Network) refers to the entire network infrastructure within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office building, or campus.
-
- It encompasses all networking technologies and devices within that specific area, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Token Ring.
-
- Definition:
-
- LAN defines the boundary and extent of the network, specifying the range within which devices are interconnected.
-
- It includes various networking components like routers, switches, cables, and network interface cards (NICs).
-
- Functionality:
-
- LAN facilitates communication and resource sharing among devices within the same geographical location, enabling tasks such as file sharing, printer sharing, and internet connectivity.
-
- It enables efficient data exchange and collaboration among connected devices, improving productivity and workflow within the local environment.
When it comes to Ethernet the key differences:
-
- Technology:
-
- Ethernet specifically refers to the networking technology used for communication within a LAN.
-
- It defines standards for physical wiring, signaling, and data transmission at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model.
-
- Standards:
-
- Ethernet standards specify parameters such as data transfer rates, frame formats, and access methods for devices within a LAN.
-
- These standards ensure interoperability and compatibility among Ethernet-enabled devices, allowing seamless communication and data exchange.
-
- Implementation:
-
- Ethernet technology is implemented through various hardware components, including Ethernet cables, network interface cards (NICs), switches, and routers.
-
- It provides a reliable and scalable solution for local network connectivity, supporting different data rates and network topologies based on specific requirements.
In summary, while LAN defines the overall network infrastructure within a limited geographic area, Ethernet specifically refers to the technology and standards used for communication within that LAN. LAN encompasses various networking technologies, while Ethernet is a specific technology within the LAN framework, defining standards for data transmission and connectivity.

Are LAN and Ethernet the Same Thing?
No, LAN and Ethernet are not the same thing.
A Local Area Network (LAN) refers to the entire network infrastructure within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office building, or campus. It encompasses various networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Token Ring, and defines the scope of interconnected devices within that specific area. LAN facilitates communication and resource sharing among devices, enabling tasks like file sharing, printer sharing, and internet connectivity.
Ethernet, on the other hand, specifically refers to the networking technology used for communication within a LAN. It defines standards for physical wiring, signaling, and data transmission at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. Ethernet standards ensure interoperability and compatibility among devices within the LAN, implemented through hardware components like Ethernet cables, network interface cards (NICs), switches, and routers.
In essence, Ethernet is a specific technology within the LAN framework, defining standards and protocols for data transmission, while LAN refers to the overall network infrastructure within a confined geographical area, encompassing various networking technologies beyond just Ethernet.
What Do LAN Cables Do?
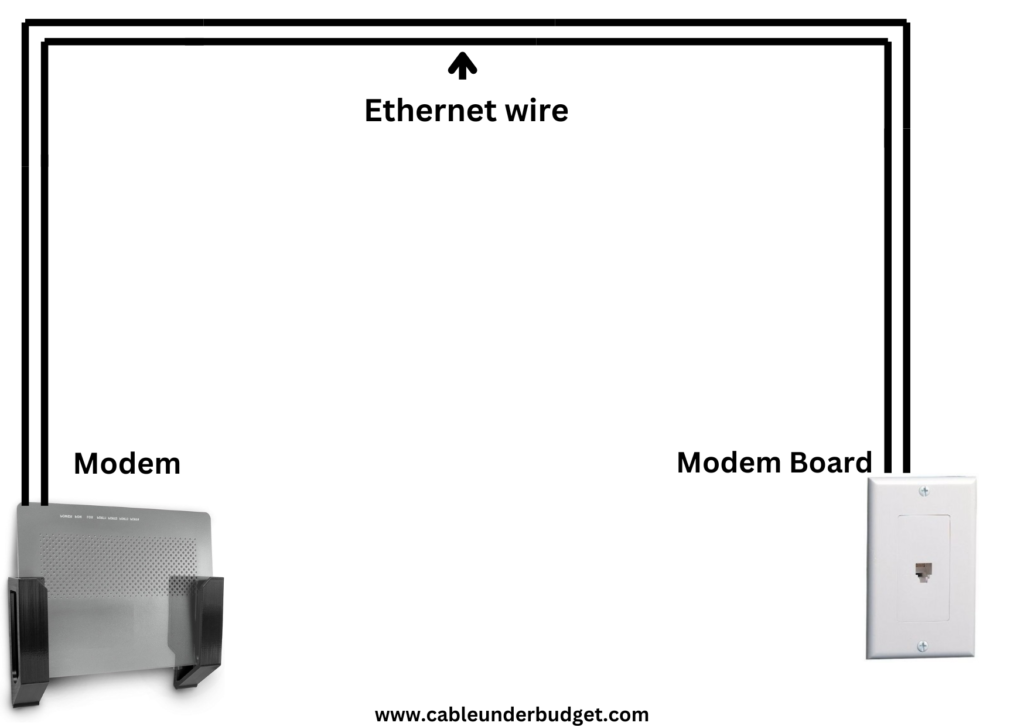
LAN cables, also known as Ethernet cables, serve the crucial function of establishing physical connections between devices within a Local Area Network (LAN). These cables facilitate data transmission between computers, printers, routers, switches, and other network devices, enabling communication and resource sharing within the LAN environment. LAN cables transmit data signals using electrical impulses over copper wires or light signals over fiber optic cables, depending on the type of cable used. By providing the physical medium for data exchange, LAN cables play a vital role in ensuring reliable and efficient communication within the network, supporting tasks such as file sharing, printer sharing, internet connectivity, and other network-dependent applications.
Also Read: Ethernet Cable vs. Data Cable
Conclusion
In conclusion, while LAN and Ethernet are closely related concepts in networking, they are not synonymous. LAN refers to the overall network infrastructure within a limited geographic area, encompassing various networking technologies beyond just Ethernet. On the other hand, Ethernet specifically denotes the technology and standards used for communication within a LAN, defining parameters for physical wiring, signaling, and data transmission. While LAN defines the scope and extent of interconnected devices within a specific area, Ethernet delineates the protocols and mechanisms for data exchange within that LAN. Understanding the distinctions between LAN and Ethernet is crucial for effectively designing, implementing, and managing local area networks.