Contents
- 1 What is Attenuation in Networking Cables
- 2 What is Attenuation
- 3 Causes of Attenuation
- 4 Types of Attenuation
- 5 Effects of Attenuation
- 6 Measuring Attenuation
- 7 Formula of Attenuation
- 8 Preventing Attenuation
- 9 Attenuation in Different Cable Types
- 10 Attenuation in Wireless Networks
- 11 Educational Resources on Attenuation
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 Unique FAQs
- 13.1 How does attenuation differ between coaxial and fiber optic cables?
- 13.2 Can attenuation be completely eliminated in networking cables?
- 13.3 What role does impedance matching play in attenuating signals?
- 13.4 How do signal repeaters help mitigate attenuation?
- 13.5 Are there specific tools for measuring attenuation in networking cables?
What is Attenuation in Networking Cables
Networking cables serve as the lifeline of modern communication systems, enabling the seamless transfer of data acrosas vast distances. However, amidst this intricate web of connectivity, there exists a phenomenon known as attenuation, which can significantly impact the performance and reliability of these networks.
What is Attenuation
Attenuation refers to the gradual loss of signal strength as it travels along a transmission medium, such as networking cables. In simpler terms, it’s like the weakening of a radio signal as you move away from the broadcasting tower. This weakening is a natural consequence of the signal encountering various obstacles and resistance along its path.
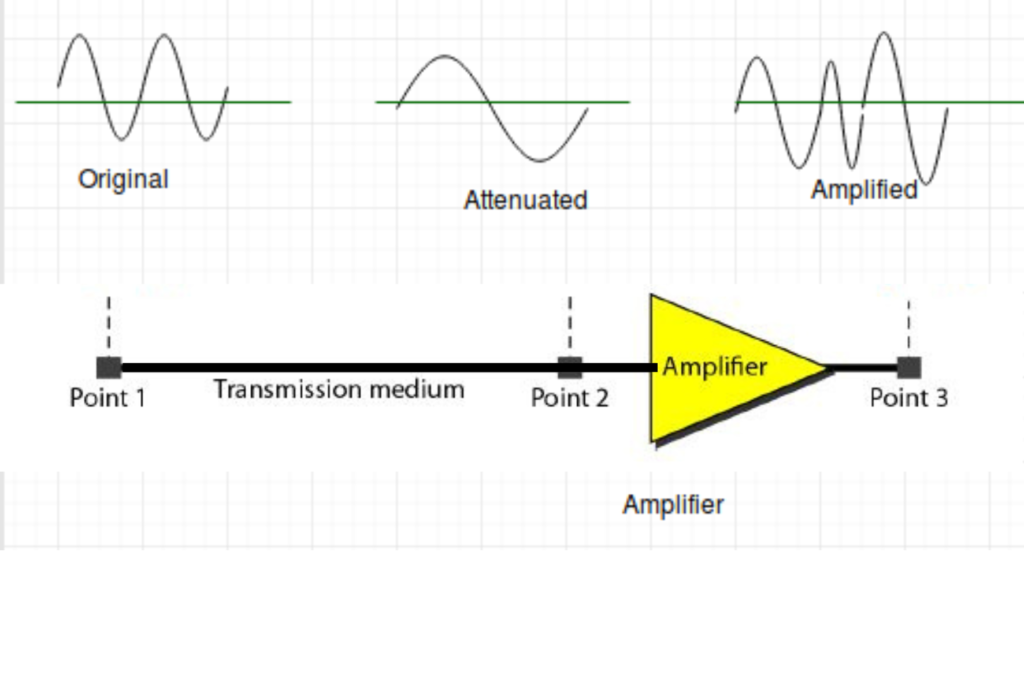
Causes of Attenuation
Several factors contribute to attenuation in networking cables:
Distance
The longer the cable, the greater the attenuation. This is due to the resistance encountered by the signal as it travels through the conductor.
Impedance
Mismatched impedance between cables and devices can lead to reflections and increased attenuation.
Interference
External sources of electromagnetic interference, such as power lines or electronic devices, can disrupt the signal and exacerbate attenuation.
Cable Quality
The quality of the cable itself plays a crucial role in determining attenuation levels. Poorly constructed or damaged cables are more prone to signal loss.
Types of Attenuation
Attenuation can manifest in various forms:
Signal Loss Over Distance
As mentioned earlier, signal strength naturally diminishes over long distances due to resistance in the transmission medium.
Signal Distortion
In addition to losing strength, signals can also suffer from distortion, resulting in errors in data transmission.
Insertion Loss
This refers to the loss of signal strength when a device, such as a connector or splitter, is inserted into the cable line.
Effects of Attenuation
The consequences of attenuation include:
- Reduced Signal Strength: Weakened signals may struggle to reach their intended destinations, leading to communication breakdowns.
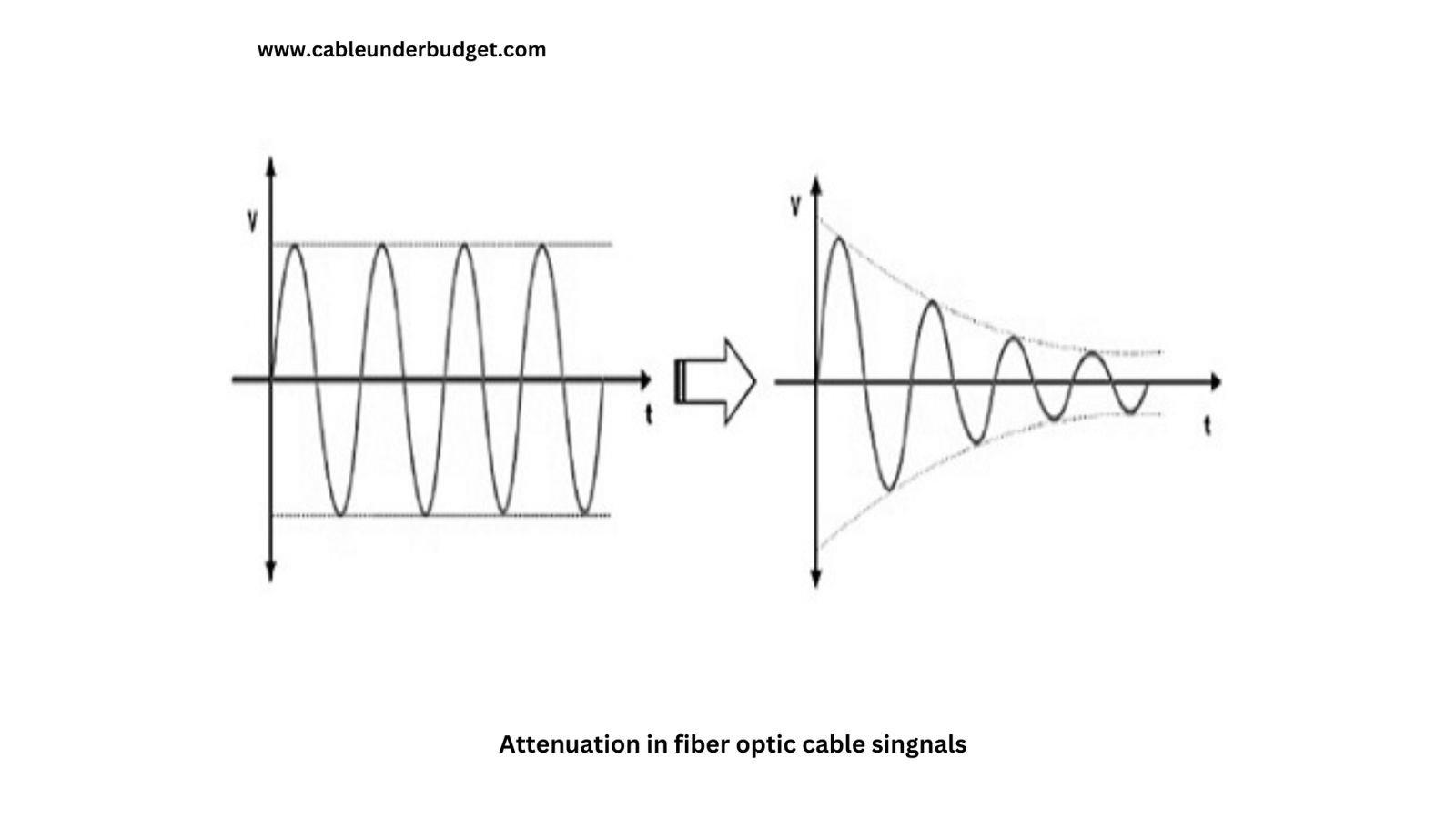
- Data Transmission Errors: Distorted signals can result in corrupted data packets, necessitating retransmission and potentially slowing down network performance.
Measuring Attenuation
Attenuation is typically measured in decibels (dB) and can be assessed using specialized tools such as network analyzers or time-domain reflectometers.
Formula of Attenuation
The formula for attenuation can vary depending on the specific context and parameters involved, but a general formula commonly used to calculate attenuation in networking cables is:
Attenuation (dB) = 10 * log10 (P1 / P2)
Where:
- Attenuation (dB) is the attenuation in decibels.
- P1 is the power of the signal at the input (initial) point.
- P2 is the power of the signal at the output (final) point.
This formula essentially calculates the ratio of the initial signal power to the final signal power in logarithmic form, providing a measure of how much the signal strength decreases as it travels through the cable.
Preventing Attenuation
While attenuation cannot be entirely eliminated, it can be mitigated through various measures:
- Proper Cable Installation: Ensuring cables are installed correctly and securely can minimize signal loss.
- Signal Boosters and Repeaters: These devices amplify signals to compensate for attenuation over long distances.
- Quality Cables and Connectors: Investing in high-quality cables and connectors reduces the risk of attenuation due to poor construction or damage.
Attenuation in Different Cable Types
Different types of cables exhibit varying degrees of attenuation:
- Coaxial Cables: Widely used in cable television and internet connections, coaxial cables are relatively resistant to attenuation.
- Twisted Pair Cables: Commonly found in Ethernet networks, twisted pair cables are susceptible to attenuation, especially over long distances.
- Fiber Optic Cables: With their ability to transmit data using light pulses, fiber optic cables experience minimal attenuation, making them ideal for long-distance transmissions.
Future Developments in Attenuation Management
Advancements in cable technology and signal enhancement techniques continue to push the boundaries of attenuation management. From improved insulation materials to innovative signal processing algorithms, ongoing research aims to minimize attenuation and maximize network reliability.
Attenuation in Wireless Networks
While the principles of attenuation remain the same, wireless networks present unique challenges and mitigation strategies compared to wired counterparts. Understanding these nuances is crucial for designing robust wireless infrastructure.
Educational Resources on Attenuation
For those seeking to deepen their understanding of attenuation, a plethora of educational resources, including online courses, books, and articles, are readily available to explore this topic in greater detail.
Conclusion
Attenuation is a fundamental concept in networking that underscores the importance of maintaining signal integrity across communication channels. By acknowledging its causes, effects, and mitigation strategies, network professionals can proactively address attenuation issues and ensure optimal performance for their systems.
Unique FAQs
How does attenuation differ between coaxial and fiber optic cables?
Can attenuation be completely eliminated in networking cables?
What role does impedance matching play in attenuating signals?
How do signal repeaters help mitigate attenuation?
Are there specific tools for measuring attenuation in networking cables?


Pingback: The Miracle of Sound Attenuation Blanket| Say Goodbye to Noise Pollution 1