Contents
What is LAN Cable
A LAN (Local Area Network) cable, also commonly referred to as an Ethernet cable or network cable, is a type of cable used to connect devices within a local area network. These cables typically have connectors on both ends that allow them to be plugged into network devices such as computers, routers, switches, and network-enabled printers.

LAN cables come in various categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each with different specifications regarding data transmission speed and bandwidth. They use twisted pairs of copper wires to transmit data signals between devices.
LAN cables are essential for establishing wired network connections, providing reliable and high-speed communication between devices within a local network. They are widely used in homes, offices, and other environments where multiple devices need to be connected to a network.
Types of LAN Cable
Here are some common types of LAN cables:
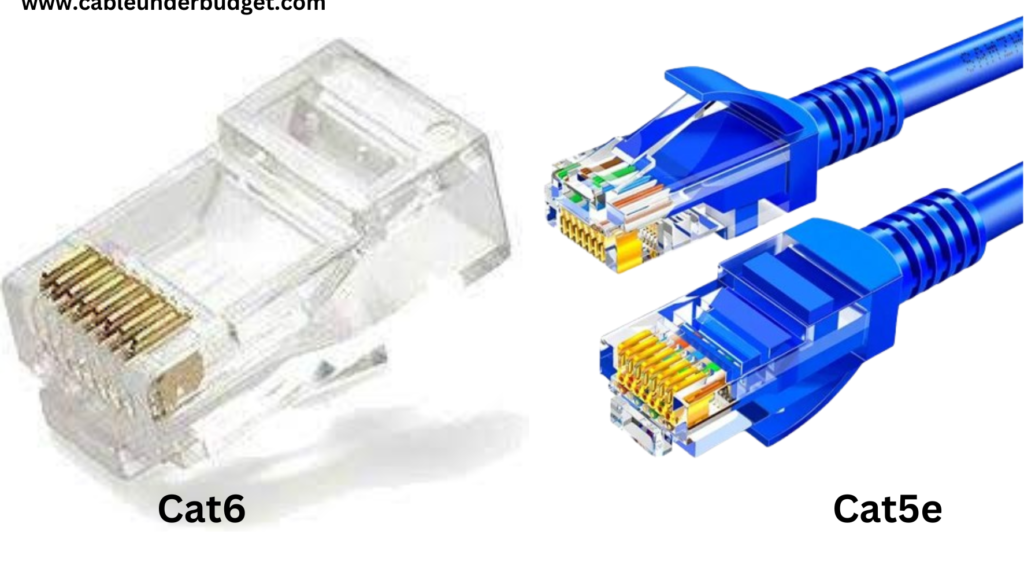
Ethernet cable
Ethernet Cable (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat8): These cables use twisted pairs of copper wires and come in various categories offering different speeds and bandwidths.
- Cat5e (Category 5e): This type of cable supports speeds up to 1 Gbps and is suitable for most home and small office networks.
- Cat6 (Category 6): Cat6 cables offer higher performance than Cat5e, supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances.
- Cat6a (Category 6a): Cat6a cables are similar to Cat6 but provide better performance and support speeds up to 10 Gbps over longer distances.
- Cat7 (Category 7): Cat7 cables are designed to support even higher speeds, up to 10 Gbps, and offer better shielding against interference.
- Cat8 (Category 8): Cat8 cables are the latest standard, capable of supporting speeds up to 25 or 40 Gbps over short distances.
Fiber Optic Cable:
Fiber optic cables use glass or plastic fibers to transmit data using light signals. They offer high speeds and are immune to electromagnetic interference.
Coaxial Cable:
Coaxial cables have a central conductor surrounded by insulation, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer. They’re commonly used for cable television and broadband internet connections.
Advantages & disadvantages of LAN Cable
Advantages of LAN cabling:
- Reliability: LAN cabling offers a stable and reliable connection, less prone to interference or signal loss compared to wireless networks.
- Security: Wired LAN connections are generally more secure than wireless networks as they are harder to intercept without physical access to the cables.
- High speed: LAN cables support high-speed data transmission, suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming and large file transfers.
- Low latency: Wired LAN connections typically have lower latency compared to wireless networks, important for real-time applications such as online gaming and video conferencing.
- Scalability: LAN cabling infrastructure can be easily expanded by adding more cables or switches, allowing for the growth of the network as needed.
Disadvantages of LAN cabling:
- Installation complexity: Installing LAN cables can be labor-intensive and may require professional expertise, especially for large-scale installations or in buildings with complex layouts.
- Limited mobility: Devices connected via LAN cables are stationary and lack the mobility offered by wireless connections, which can be a drawback in certain environments or for mobile devices.
- Physical constraints: LAN cables are susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as bending, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, requiring proper installation and maintenance.
- Cost: Setting up a LAN cabling infrastructure can be initially expensive, requiring the purchase of cables, connectors, switches, and other networking equipment. Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs may also be incurred.
- Infrastructural limitations: LAN cabling requires physical infrastructure such as cables, connectors, and networking devices, which may not be feasible or practical in certain environments, such as historic buildings or outdoor locations.
Overall, while LAN cabling offers numerous advantages in terms of reliability, security, and speed, it also comes with drawbacks such as installation complexity, limited mobility, and cost. The choice between LAN cabling and wireless networking depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the network, budget constraints, and environmental considerations.
ALSO READ: Fiber Optic Cable Installtion
Are LAN and Ethernet cable are Same?
LAN (Local Area Network) and Ethernet are not exactly the same thing, but they are closely related. Ethernet is a specific type of networking technology used within LANs.
A LAN refers to a network that connects devices in a limited geographical area, such as within a home, office building, or campus. It encompasses the infrastructure, protocols, and devices used to facilitate communication and resource sharing among connected devices.
Ethernet, on the other hand, is a widely used standard for wired LAN communication. It defines the physical and data link layers of the OSI model and specifies the protocols and hardware required for transmitting data over Ethernet networks. Ethernet typically utilizes twisted-pair copper cables or fiber optic cables to connect devices within a LAN.
So, while Ethernet is a common technology used within LANs, a LAN may also incorporate other networking technologies and protocols besides Ethernet. Therefore, while closely related, LAN and Ethernet are not exactly the same thing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LAN cables play a crucial role in establishing wired network connections within local area networks (LANs). They provide a reliable, secure, and high-speed means of transmitting data between devices such as computers, routers, switches, and printers. Despite the rise of wireless technologies, LAN cables remain essential for applications requiring stable connections, low latency, and high bandwidth, such as gaming, video streaming, and enterprise networking. While Ethernet cables are the most common type of LAN cable, other options such as fiber optic and coaxial cables also exist to meet specific network requirements. Overall, LAN cables continue to be a fundamental component of modern networking infrastructure, offering robust connectivity and facilitating efficient communication in various environments.

